HSA_CIRC_0000234 FUNCTIONS AS A COMPETITIVE ENDOGENOUS RNA TO REGULATE VAMP3 EXPRESSION BY SPONGING MIR-142-3P IN GASTRIC CANCER
Lei Peng*, Guoxin Zhang
Department of Gastroenterology, The First Affiliated Hospital with Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, China
BACKGROUND: Emerging evidence points towards an important role of circular RNAs (circRNAs) in the tumorigenesis and progression of gastric cancer (GC). Hsa_circ_0000234 has recently been reported to be differentially expressed in GC microarray but the mechanism of it seems unclear.
METHODS: qRT-PCR was used to detect the expression of hsa_circ_0000234, miR-142-3p and VAMP3 in tumor tissues and cell lines of GC. The CCK-8 assay, colony formation, Transwell assay and wound healing assay were used to evaluate the proliferation, invasion and migration of GC cells, respectively. Bioinformatics analysis and luciferase reporter assay were performed to disclose the interaction between hsa_circ_0000234, miR-142-3p and VAMP3. Western blot and immunofluorescence were applied to assess the downstream signaling of VAMP3.
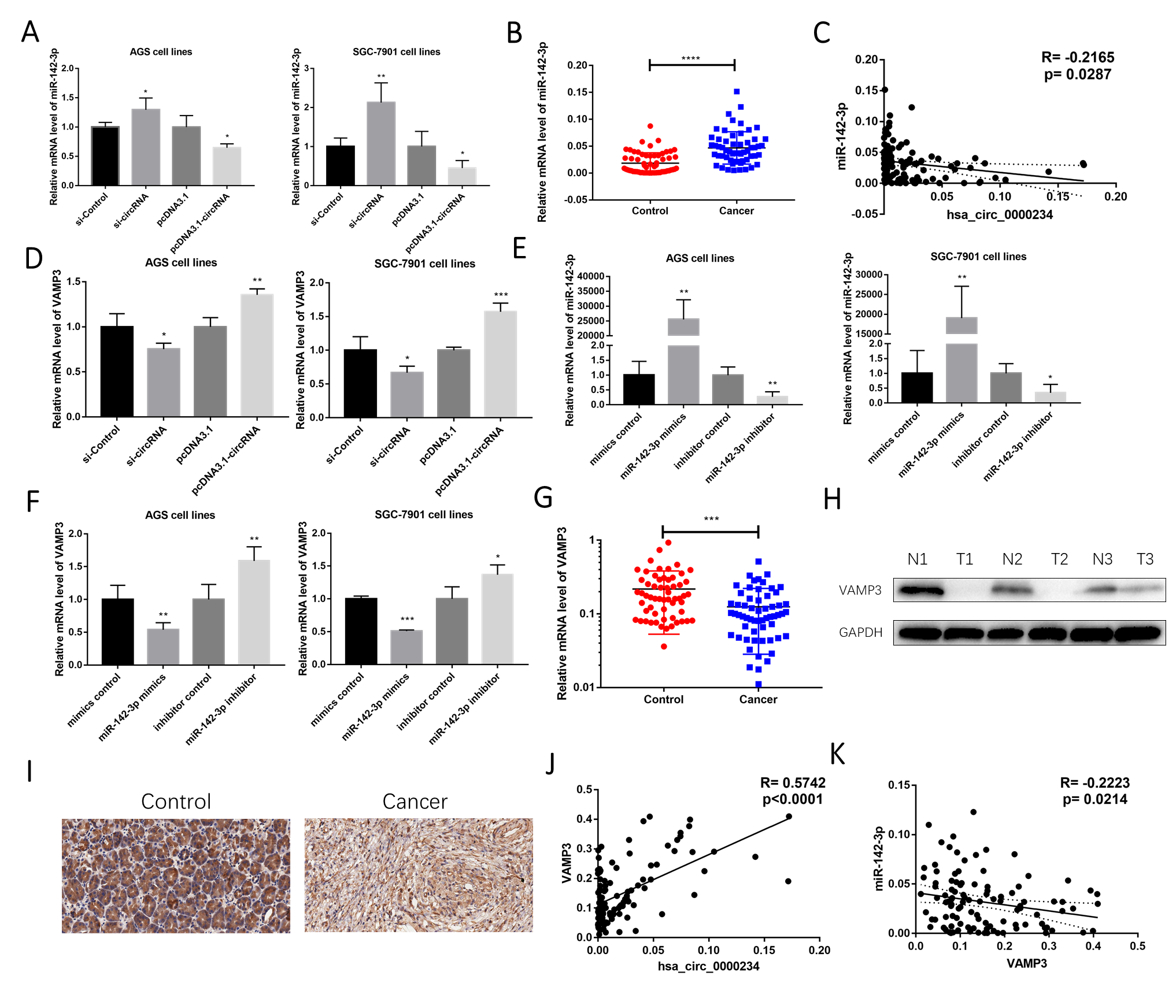
RESULTS: Hsa_circ_0000234 was found downregulated in GC tissues and cells. Low expression of hsa_circ_0000234 was significantly correlated with advanced TNM stage and lymphatic metastasis. Gain- and loss-of-function of hsa_circ_0000234 revealed that hsa_circ_0000234 functioned as a ceRNA for miR-142-3p to facilitate VAMP3 expression and then suppressing GC cell proliferation, invasion and migration, and promoting apoptosis. Furthermore, hsa_circ_0000234 overexpression suppressed tumor growth and inhibited the expression of miR-142-3p, but increased the expression of VAMP3 in vivo.
CONCLUSIONS: Our results suggest a potential ceRNA regulatory network involving hsa_circ_0000234 regulates VAMP3 expression by competitively binding endogenous miR-142-3p in tumorigenesis and progression of GC. This mechanism may contribute to a better understanding of GC pathogenesis and provide potential therapeutic strategy for GC.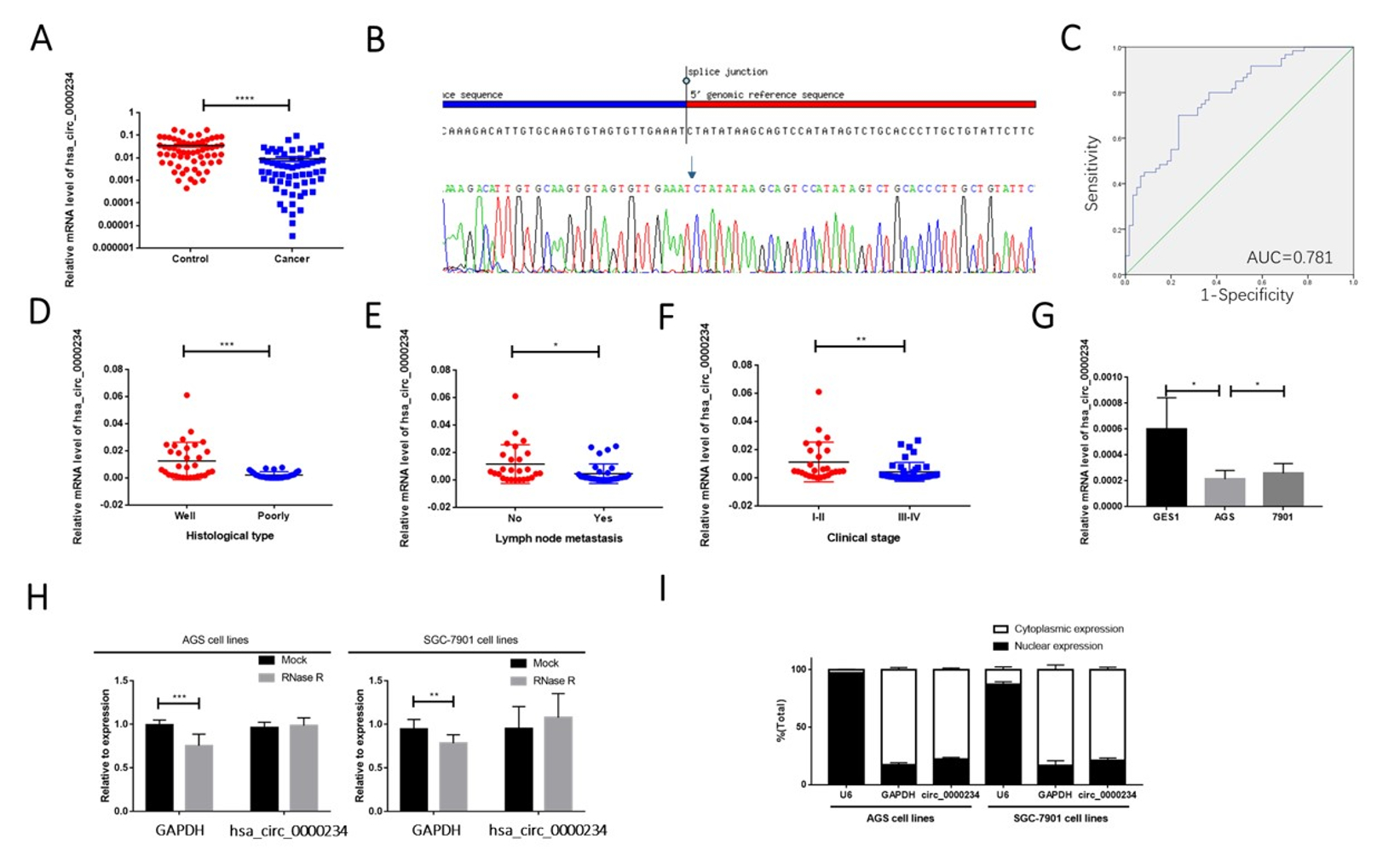
Back to 2019 Abstracts




