EXOSOMAL MIR-15B-3P PROMOTES THE DEVELOPMENT OF GASTRIC CANCER BY TARGETING DYNLT1
Shuchun Wei*, Guoxin Zhang
Department of Gastroenterology, First Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing, China
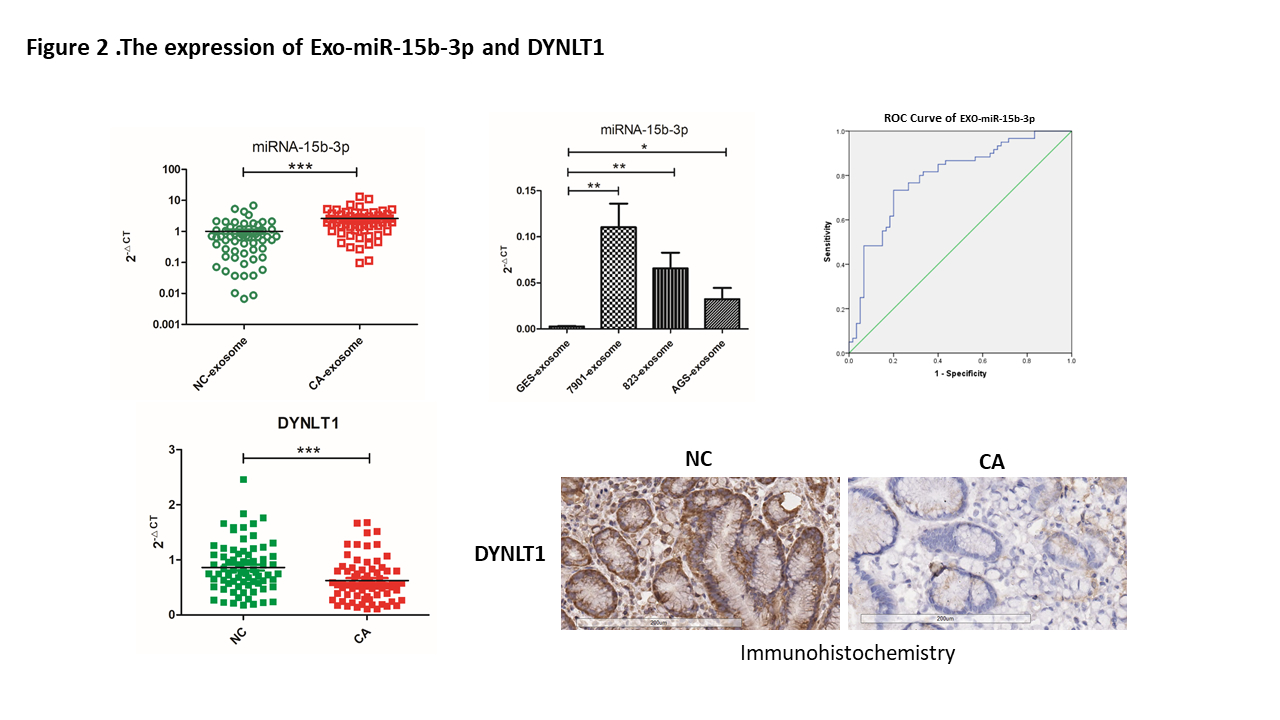
BACKGROUND: Exosomes, a type of novel signaling molecules, are critically involved in tumor growth, metastasis, and therapy resistance.The roles of miRNAs in the development of cancer have made them promising tools for novel diagnostic and therapeutic approaches. Here, We found that the exosomes in the plasma of 72 gastric cancer patients and the culture supernatants of GC cells was significantly higher than that of 72 healthy volunteers and gastric epithelial cell line-GES-1. In particular, the expression of exosomal miR-15b-3p was significantly higher than that of non-cancer individuals and GES-1.
METHODS: Exosomes were successfully isolated by ultracentrifugation and exosomes morphologies and sizes were determined by transmission electron microscopy and Nanosight Analysis. The protein markers of exosomes (CD9,CD63,TSG101) were detected by Western blot. Real-time quantitative PCR was used to detect the expression of exosomal miR-15b-3p. Fluorescent PKH-67 labeled exosomes and Cy3-Exo-miR-15b-3p mimics derived from The GC cell lines SGC-7901 and BGC-823 could be taken up and internalized by recipient cells. Thereafter,qRT-PCR, CCK8, Colony formation, EDU,Transwell, Wound-healing assay, Flow cytometric analyses of cell cycle and apoptosis were performed to assess the role of Exo-miR-15b-3p in vitro. BALB/c nu/nu mice tumor model was constructed to evaluate tumor growth and metastasis in vivo. The expression of DYNLT1 was assessed by qRT-PCR,WB and immunohistochemistry.
RESULTS: The GC cell lines SGC-7901 and BGC-823 derived exosomes were internalized by receipt cells via caveolin- and lipid raft-dependent endocytosis, which allowed the transfer of miR-15b-3p. Exo-miR-15b-3p enhanced the proliferation, migration and invasion in vitro and vivo. The area under the ROC curve (AUC) of Plasma Exo-miR-15b-3p was 0.80, and Exo-miR-15b-3p may closely related to the occurrence and development of gastric cancer.The dual-luciferase reporter assay indicated that miR-15b-3p inhibits DYNLT1 expression by directly targeting its 3'-UTR. The expression levels of DYNLT1 were significantly decreased in the GC cells, the tumor tissues of 72 gastric cancer patients and the mice treated with Exo-miR-15b-3p .
CONCLUSIONS:Our results are the first to show that exosomal miR-15b-3p promotes the growth and metastasis of gastric cancer by directly targeting the promoter of DYNLT1 in vitro and vivo. In addition ,the plasma Exo-miR-15b-3p can be used as a potential marker for the diagnosis and prognosis of gastric cancer, providing new ideas for the treatment of gastric cancer.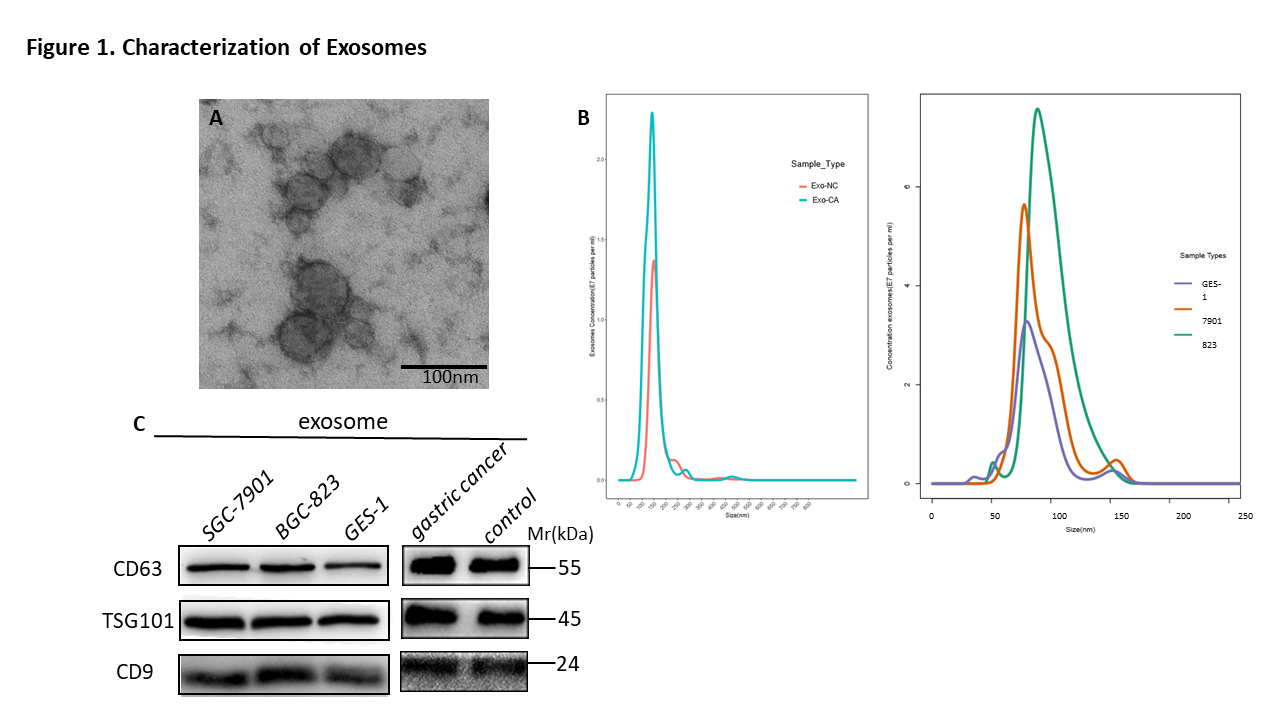
Back to 2019 Abstracts




