SIMULTANEOUS LAPAROSCOPIC PYLOROPLASTY AND GASTRIC STIMULATOR INSERTION IS AN EFFECTIVE PALLIATIVE OPTION FOR TREATMENT OF MEDICALLY REFRACTORY GASTROPARESIS
Daniel A. Barrera*1, Aishwarya Rajagopal4, Ahmed M. Zihni2,3, Ashwin A. Kurian2
1Centura Health St. Anthony Hospital, Denver, CO; 2SurgOne Foregut Institute, Denver, CO; 3The Oregon Clinic, Portland, OR; 4University of Colorado, Boulder, CO
INTRODUCTION
Gastroparesis is a chronic incurable gastric motility disorder defined by delayed gastric emptying and symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, bloating and abdominal pain. Surgical options are aimed towards palliation of symptoms and include pyloroplasty, gastric stimulator insertion and gastrectomy. The palliation from pyloroplasty and gastric stimulator may be synergistic. Concerns exist regarding the possibility of stimulator infection when performing both procedures simultaneously. We present our experience of performing combined laparoscopic pyloroplasty and gastric stimulator insertion.
METHODS
Gastroparetic patients diagnosed based on solid gastric scintigraphy or endoscopic evidence of retained food after prolonged fasting underwent combined laparoscopic Heineke-Mikulicz pyloroplasty and gastric stimulator insertion between July 2016 to October 2018 by a single surgeon. Patient demographics, pre- and post-operative symptom scores and outcomes were collected. All patients completed pre- and post-operative symptom score surveys. Results were analyzed using statistical tests as appropriate. P values <0.05 were considered significant.
RESULTS
Twenty-three patients underwent simultaneous pyloroplasty and gastric stimulator insertion. Two patients were male (9%) and twenty-one were female (91%). Mean age was 44.4▒12.7 years and mean BMI was 24.7▒4.5. Sixteen patients (70%) were idiopathic, six patients (27%) were diabetic, one patient (4%) had post-operative gastroparesis and. All patients had failed medical management. Eight patients (35%) had prior pyloric Botox injections. All were na´ve to surgical treatments for gastroparesis.
Median hospital stay was 2▒1 days. Four patients (17%) required readmission or ED visit within 30 days. One patient (4%) experienced a contained leak which was managed non-operatively. One stimulator infection (4%) was reported in follow-up and required explantation. Four patients (17%) required revision of the implant - two for abnormal impedance and recurrent symptoms, and two for discomfort due to implant flipping in the subcutaneous pocket. Patient symptoms significantly improved in all gastroparesis-specific categories (Table). Overall mean composite score (Gastroparesis Cardinal Symptom Index: GCSI-2W) decreased from 3.82▒0.85 to 2.53▒1.15 (p value 0.0003). Mean duration of follow-up was 13.6 weeks (3 weeks - 56 weeks).
CONCLUSIONS
Combined laparoscopic Heineke-Mikulicz pyloroplasty with gastric stimulator placement is a safe and effective minimally invasive procedure suitable for first line surgical treatment of refractory gastroparesis.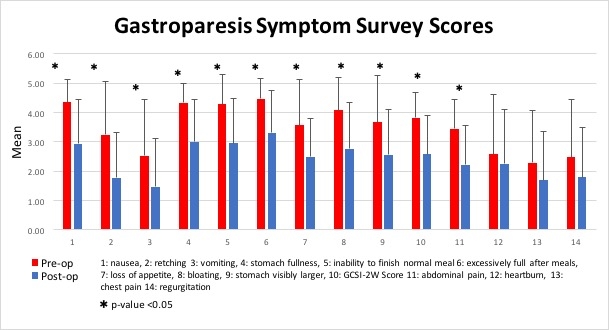
Back to 2019 Abstracts




