|
Back to 2014 Annual Meeting Posters
Robotic Pancreaticoduodenectomy: Comparison of Complications and Cost to the Open Approach
Samuel W. Ross*, Ramanathan Seshadri, Bindhu Oommen, Erin M. Hanna, Ryan Z. Swan, Amanda Walters, Vedra a. Augenstein, David Sindram, B. Todd Heniford, David a. Iannitti, John B. Martinie
Department of General Surgery, Carolinas Medical Center, Charlotte, NC
Introduction:
Robotic pancreaticoduodenectomy (RP) has shown some advantages over open pancreaticoduodenectomy (OP) but no data has been published providing a cost comparison. We hypothesized that RP would initially be more expensive but patients would have decreased complications and follow-up costs.
Methods:
This is a retrospective cohort study of all pancreaticoduodenectomies performed at a single quaternary cancer referral center from August 2012 to July 2013. Patient demographics, comorbidities, operative characteristics, complications, and charge data were recorded for OP and RP, and then compared using standard statistical methods. All conversions from RP to OP were analyzed with intention to treat. Statistical significance was set to p≤0.05.
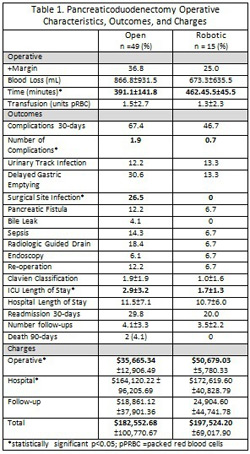
Results:
There were 64 pancreaticoduodenectomies: 15 RP and 49 OP. There were two conversions in the RP group due to vein resection or repair. Patients undergoing OP were similar to RP: age (62.1±12.9vs64.4±10.3), male(44.9%vs66.7%), BMI(26.7±5.5vs25.7±4.1kg/m2), Charlson Comorbidity Index(2.9±1.7vs2.2±1.4), ASA score III (65.3vs60.0%) malignant etiology(81.6%vs80.0%), neoadjuvant chemotherapy (12.8%vs15.4%); all non-significant. Operative characteristics, patient outcomes, and charges are recorded in Table 1. OP and RP had similar rates of R0 resection, length of stay (LOS), readmission, total charges, and mortality, but OP had significantly more complications and ICU LOS (p<0.05).
Conclusion:
Patients undergoing RP have equivalent rates of R0 resection as OP, and benefit from decreased number of complications, surgical site infections, and LOS in the ICU. As expected, operative time and cost are significantly increased in RP. However, once cost of complications and follow-up are incorporated, total charge to the patient is not statistically significantly different.
Back to 2014 Annual Meeting Posters
|


