
|
 |
Back to Annual Meeting Posters
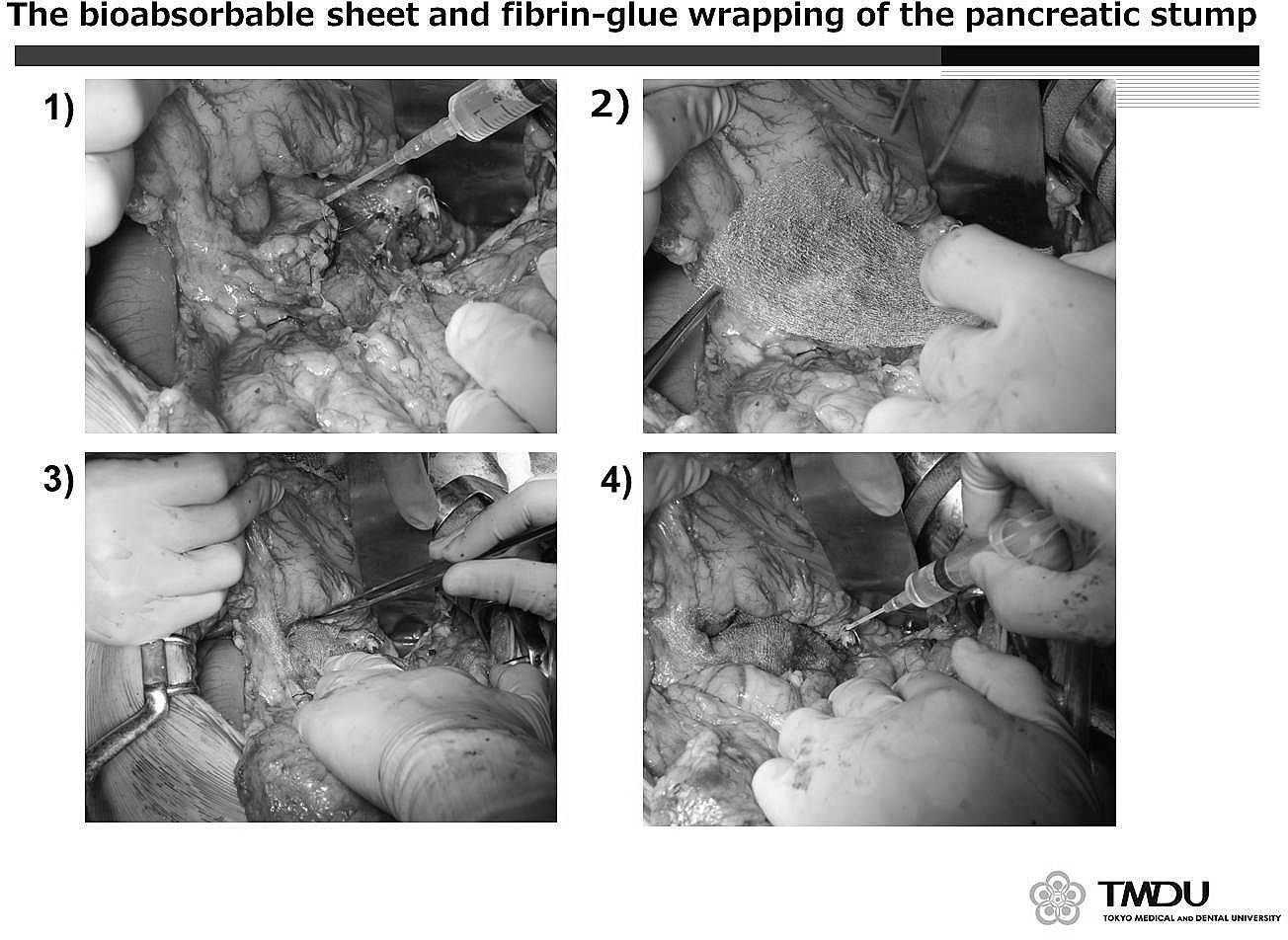
Efficacy of Wrapping the Pancreatic Stump With a Bioabsorbable Sheet and Fibrin Glue After Distal Pancreatectomy
Daisuke Ban*, Kota Sato, Satoshi Matsumura, Takumi Irie, Takanori Ochiai, Atsushi Kudo, Noriaki Nakamura, Shinji Tanaka
Department of Hepato-Biliary-Pancreatic Surgery, Tokyo Medical and Dental University, Tokyo, Japan
Background: Distal pancreatectomy (DP) is a simple operative procedure. However, morbidity associated with pancreatic fistula has remained unresolved. In 25 of 70 DPs, we wrapped the pancreatic stump in a bioabsorbable sheet with fibrin glue. The aim of this study was to evaluate the efficacy of our wrapping method.
Method: Between January 2006 and October 2012, 70 laparoscopic and open patients underwent DP. Pancreatic stump closure was achieved with a stapler or by conventional hand-sewn closure. In the wrapping group, the pancreatic stumps were wrapped with a polyglycolic acid felt bioabsorbable sheet (0.15 mm thick), and fibrin glue was sprayed onto the wrapped stump. Pancreatic fistulas were classified according to the grading system of ISGPF. The primary endpoint was the occurrence of a clinical pancreatic fistula, including Grade B and C.
Result: Of the patients, 25 (36%) underwent pancreatic stump wrapping, and 45 (64%) had no additional treatment after pancreatic stump closure (non-wrapped-). In the wrapped group, Grade A, B, and C pancreatic fistulas occurred in 7 (28%), 2 (8%), and 0 patients, respectively. In the non-wrapped group, Grade A, B, and C pancreatic fistulas occurred in 6 (13%), 17 (38%), and 1 (2%) of subjects, respectively. The incidence of clinical pancreatic fistula in wrapped patients was significantly lower than that in unwrapped patients (p = 0.004). The average of the amylase value in pancreatic drains in the unwrapped and wrapped group was 3893 IU/L and 15562 IU/L on postoperative day (POD) 1, 1401 IU/L and 1736 IU/L on POD 3, respectively. On POD 1, the drain amylase value in wrapped patients was significantly lower than that in unwrapped patients (p=0.004). Other clinical features and treatments including age, sex, body mass index, primary disease, American Society of Anesthesiologists classification, previous laparotomy, intraoperative bleeding, operation time, laparoscopic surgery, stump closure method, and blood transfusion were not significantly related to pancreatic fistula.
Conclusion: The present study suggests that a bioabsorbable sheet with fibrin glue wrapping has advantages after distal pancreatectomy and may reduce the incidence of pancreatic fistula.
Back to Annual Meeting Posters
|


