Background
The Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation’s Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) Plexus surgical cohort (IBD-SIRQC) was established in 2022. In this abstract, we reviewed the surgical data of the first 100 enrolled patients.
Methods
Beginning August 2022, patients were prospectively enrolled in a multicenter IRB-approved observational longitudinal cohort study at 6 centers including 17 surgeons. Inclusion criteria included adults undergoing major abdominopelvic surgery for a known diagnosis of IBD. Baseline demographics, intraoperative technical details, 30-day outcomes, and patient-reported outcomes were recorded. P-values represent Wilcoxon rank-sum test, chi-square test or Fisher’s exact test.
Results
A total of 103 patients were enrolled from 6 centers, median 13.5 (range 5 – 32) patients per center, with a median of 5 (range 1 – 15) cases per surgeon. Median age was 44 years and 52% were male. Most patients were white (85%), non-Hispanic (98%), born in the United States (96%), had commercial health insurance (77%), and were on preoperative biologic medication (55%). Sixty-four percent of patients had Crohn’s disease (CD), most commonly fibrostenotic phenotype (62%) and present in the ileum (71%) followed by colon (17.8%) and jejunum (8.2%). Thirty-five percent of patients had ulcerative colitis (UC). Most patients had severe disease (43%) involving the entire colon (61.1%), whereas fewer had proctitis only (19%) or left-sided colitis (19%).
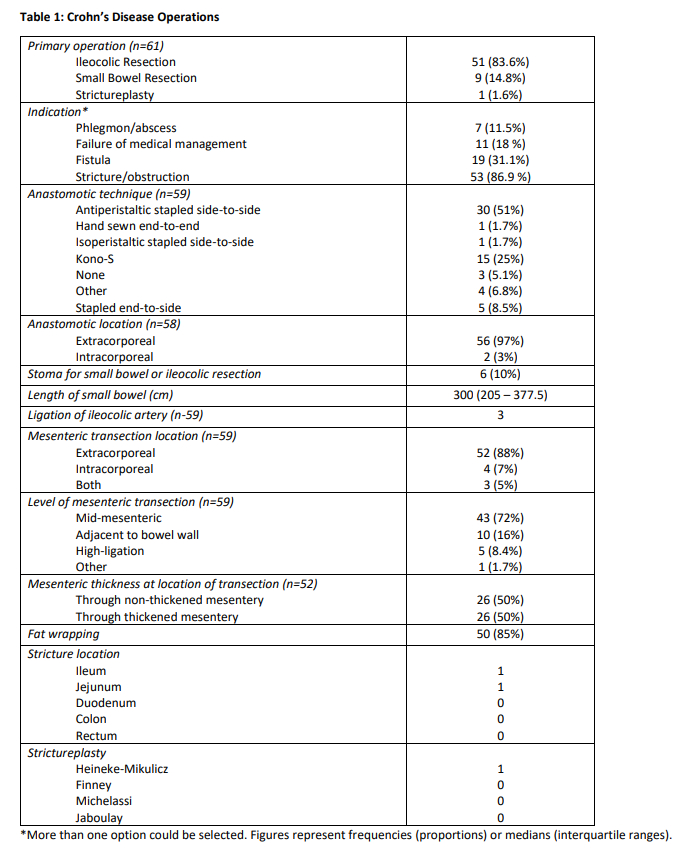
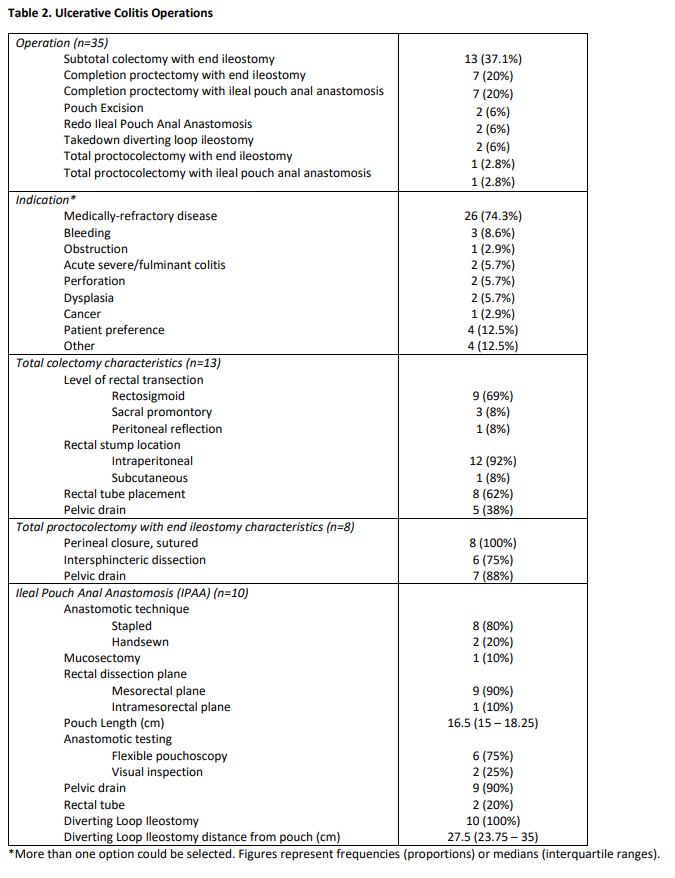
The most common operative technique was straight laparoscopy (42%) followed by open (31%), and then hybrid (12%) and robotic (12%). Overall, 7 cases were converted from a minimally invasive approach to open. All conversions were proactive, and none were reactive, in nature. Among patients with CD, the majority underwent ileocolic resection (84%) for stricture/obstruction (87%). When performing an anastomosis, 51% were stapled side-to-side and 25% were Kono-S. The mesentery was most often transected extracorporeal (88%) and through the midpoint of the mesentery (72%). Half of patients have thickened mesentery and half did not (Table 1). Among patients with UC, operations included subtotal colectomy with end ileostomy (37%) or completion proctectomy with either ileostomy (20%) or ileal pouch anal anastomosis (20%) for medically refractory disease (74%) (Table 2). At 30 days postoperatively, 22% of patients developed complications, including 1 reoperation, and 15% of patients required readmission.
Conclusions
This report describes the first 100 patients undergoing surgical intervention in the IBD-SIRQC cohort. Two-thirds of the operations are performed for CD, and were most often an ileocolic resection for fibrostenosing disease. This multicenter cohort database will provide us with data to better understand operative indications and outcomes in patients with IBD.