Background:
The incidence of anastomotic stenosis after colorectal surgery is 3% ~ 30%, it is much related to age, sex, blood circulation, inflammation, anastomotic complications and anastomotic location. Treatment methods include mechanical dilation, endoscopic incision, balloon dilation, stent placement and surgical treatment. Which always accompanied by complex operation, time-consuming, expensive and other factors. In this study, we introduced a simple, cheap and minimally invasive magnetic device for the treatment of rectal stenosis.
Methods:
The magnets used in the experiment were made of Ti-coated neodymium-iron-boron (Nd-Fe-B). They all designed of trapezoidal shape, bottom edge is 6 mm, top edge is 3 mm, height is 1.5 mm and thickness is 2 mm. Eight magnets were placed in series inside a catheter (5 mm diameter). When the magnets in the catheter were pushed out, it could automatically assembled into a ring-like structure due to the magnetic force. Four experimental dogs were anesthesia before procedure. First, ligation of the upper rectum was performed laparoscopically to establish the animal model of rectal stenosis. Secondly, delivered the catheter upon the stenosis endoscopically. A chain of magnets were pushed out of the catheter and assembled automatically into a ring like structure placed at the oral side of the stenosis. In the same way, the other set of magnets were assembled at the anal side of the stenosis. The two sets attracted and compressed the stenosis tissue under the magnetic force. After 7-, 9-, 9- and 12- days, the two sets of magnets fell off and excreted from the anus. Tissue harvest was in the 14th day post-operatively, the feasibility of this novel technique were evaluated, mechanical burst pressure were tested.
Results:
All dogs survived post-operatively, without bleeding, infection, leakage and other complications. The magnets attracted and compressed the tissue, resulting in tissue necrosis and fallen. Which was showed in 7th, 9th, 9th and 12th day post-operatively. Rectal stenosis were recanalized. The compressed tissue were harvested in 14th day, mild inflammation response can be observed histopathologically and no leakage was observed in all dogs. Burst pressure showed greater than 300mmHg.
Conclusion:
Endoscopic self-assembled magnetic compression tecnique is well indicated for the minimally invasive treatment of patients with anastomotic stenosis after rectectomy. It is especially suitable for patients with severe stenosis, suffered repeated expansion and stents which cannot achieve satisfactory results. The simple and minimally invasive surgical method greatly reduces medical costs. It may be used as a novel surgical therapy in the future.
Sponsorship?2023 Natural Science Basic Research Foundation of Shaanxi Province (2023-JC-YB-739)
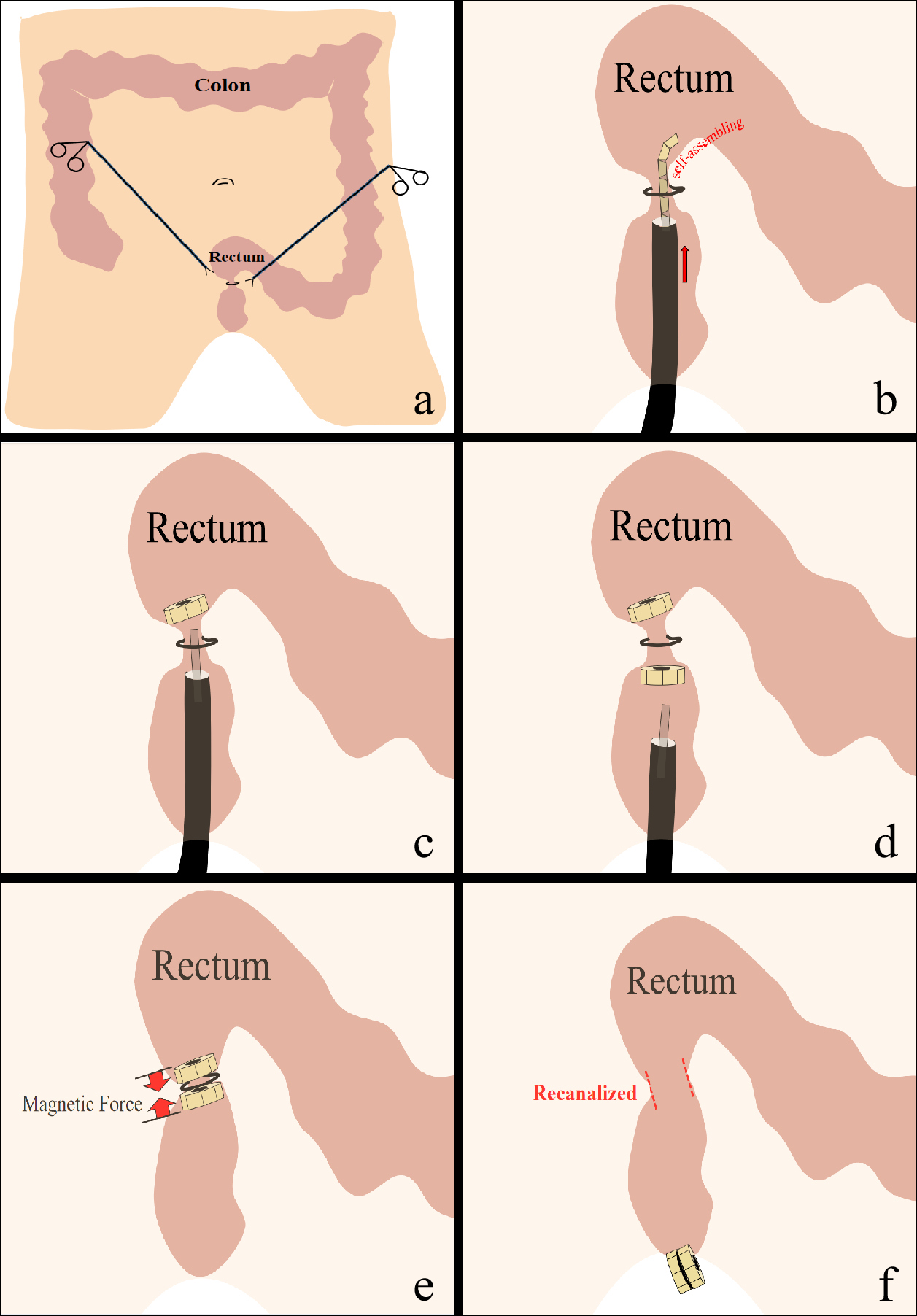
a. Laparoscopic ligation to establish the animal model of rectal stenosis. b. Endoscopic delivery of magnets in chain through the catheter. c. Magnets assembled automatically into a ring like structure placed at the oral side of the stenosis. d. The other set of magnets were assembled at the anal side of the stenosis in the same way. e. The two sets of magnets attracted and compressed the stenosis tissue under the magnetic force. f. The two sets of magnets fell off and excreted from the anus, rectal stenosis were recanalized.