Background: Bariatric surgery is the recommended for morbid obesity. Our study aim to compare and rank different bariatric surgical approaches in reducing weight parameters.
Methods: We conducted this network meta-analysis following the PRISMA-NMA guidelines and the Cochrane Handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. We searched MEDLINE, Cochrane CENTRAL, Scopus, and Web of Science databases from inception to September 2023. We extracted all outcomes as mean change from the baseline. The mean difference and 95% confidence interval were used as a summary measure. All analysis was conducted with R version 4.2.2 (2022-10-31) and R Studio version 2022.07.2 (2009-2022) RStudio, Inc.). Included surgeries were: Biliopancreatic diversion (BPD), Laparoscopic mini-gastric bypass (LMGB), Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass (RYGB), Laparoscopic Gastric Plication (LGP), Laparoscopic Greater Curvature Plication (LGCP), Duodenal-Jejunal Bypass Sleeve (DJBS), Single-anastomosis gastric bypass (SAGB), Laparoscopic vertical banded gastroplasty (LVGB), Sleeve Gastrectomy (SG), Laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding (LAGB), Gastric Imbrication, and Intra-gastric balloon (IGB).
Results: We included 59 studies in the final analysis. Our analysis showed that BPD was the best surgical technique in decreasing BMI (kg/m2) (MD = -12.49; 95%CI [-14.40, -10.58]) and RYGB was the next one in efficacy according to P-score (MD = -7.70; 95%CI [-8.62, -6.77] but the pooled analysis was heterogeneous (I2 = 74.7%). According to weight (kg), waist circumference (cm), and fat mass (kg), BPD was the best surgical technique in decreasing these parameters (MD = -41.49; 95%CI [-47.80, -35.51], MD = -29.08; 95%CI [-37.16, 21.00], and MD = -31.11; 95%CI [-38.77, -23.46]; respectively). The pooled analysis was heterogeneous except in fat mass (I2 = 60.73, I2 = 79.3%, I2 = 0%). Our network meta-analysis showed that the best surgical technique in increasing EWL (%) was LVGB (MD = 59.23; 95%CI [32.01, 86.45]) and BPD was the next one in efficacy according to P-score (MD = 51.45; 95%CI [24.28, 78.63].
Conclusion: The ranking analysis shows that Biliopancreatic diversion provides the most effective reductions in BMI followed by Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass. Laparoscopic vertical banded gastroplasty was associated with most estimated weight loss %.
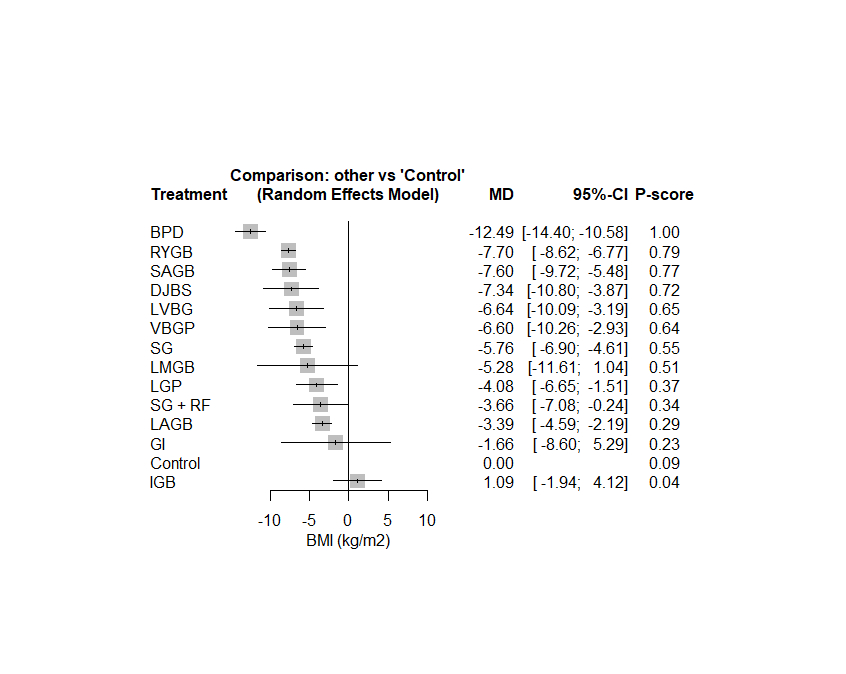
Figure 1 shows a forest plot for the ranking analysis of BMI (kg/m2) outcome
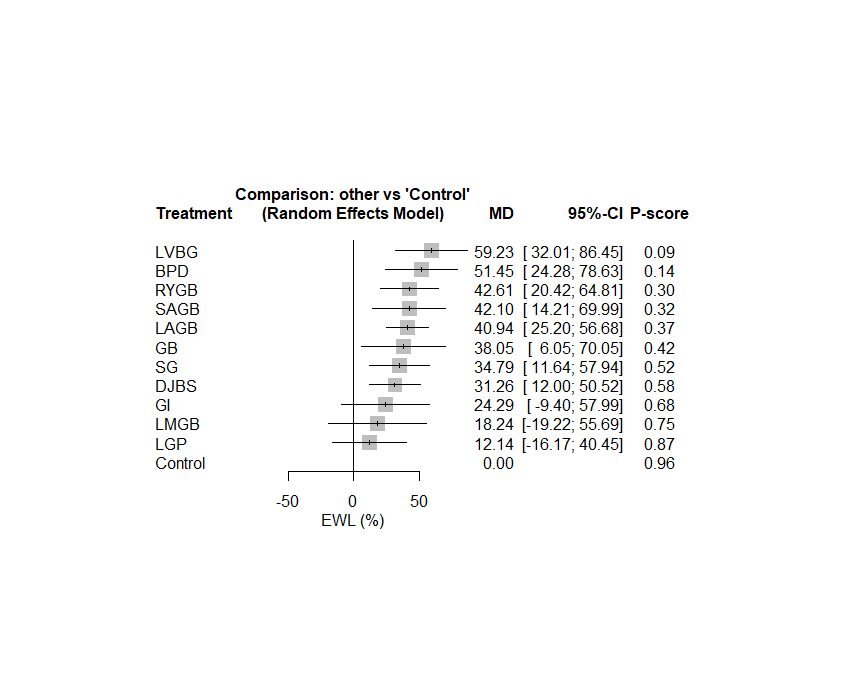
Figure 2. shows a forest plot for the ranking analysis of Excess weight loss (EWL, %) outcome