Back to 2024 Abstracts
EFFICACY OF GPOEM (GASTRIC PERORAL ENDOSCOPIC MYOTOMY) FOR REFRACTORY GASTROPARESIS: A META-ANALYSIS
Vishal Chandel
*1, Veronica West
2, Neel Chandel
31Internal Medicine, Suburban Community Hospital, East Norriton, PA; 2Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine, Philadelphia, PA; 3St Mary Medical Center, Langhorne, PA
Introduction
Symptoms of Refractory Gastroparesis (RG) don't respond adequately to treatment, due to complex pathophysiology and limited therapeutic options. Gastric per-oral endoscopic myotomy (GPOEM) is a promising novel technique for the treatment of RG with encouraging short-term efficacy rate of 80%. Our aim from this meta-analysis is to evaluate for any differences in outcomes and safety of G-POEM for RG.
Methods
We used PubMed, Medline & EMBASE before 7/1/2022, for relevant publications. Only studies presenting the clinical outcome's data of G-POEM for gastroparesis were included. Studies without data of gastroparesis cardinal symptom index (GCSI) pre- and post-procedure, data of gastric emptying scintigraphy (GES) pre- and post-procedure were excluded. Meta-analysis was done by the RevMan (Review Manager) 5.3.
Results
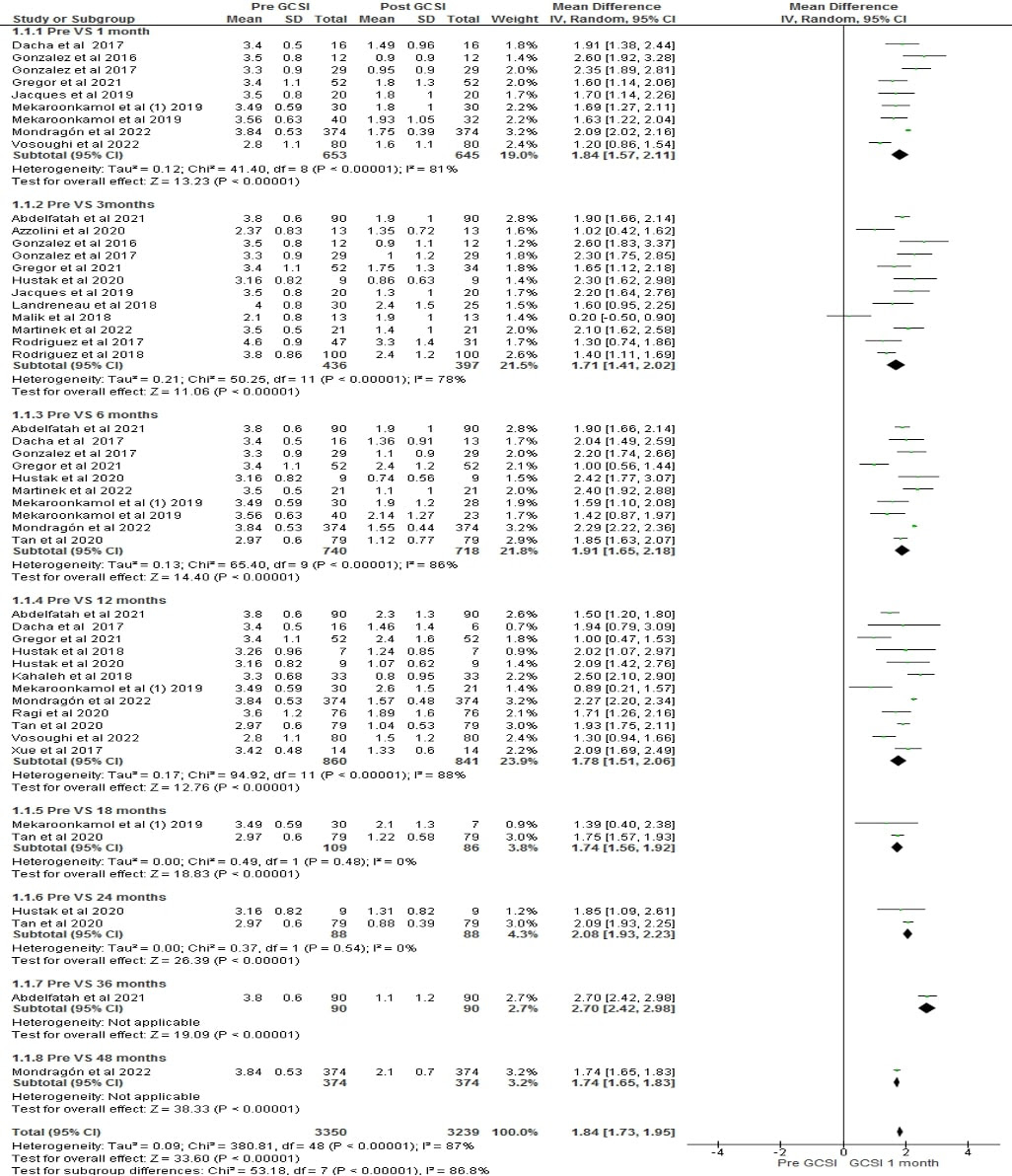
We included 29 studies with a total of 1349 patients who underwent GPOEM. Clinical success rate in all 29 studies was 75.3%, while technical success rate was 100% and mean follow-up duration was 11.59 months. Pre and Post GPOEM GCSI, GES, and sub-scores were compared. Meta analysis for GCSI included 26 studies pre-GPOEM, 9 studies from 1 month, 12 studies from 3 months, 10 from 6 months, 12 from 12 months, 2 studies each from 18 and 24 months, 1 study each from 36 and 48 months respectively. The pooled mean difference (MD) in GCSI with a 95% of confidence interval with MD was 1.84[1.57, 2.11] by Cochran Q test (p< 0.001, I
2 =81%) for 1 month, 1.71[1.41, 2.02] with (p< 0.001, I
2 = 78%) for 3 month, 1.91[1.65, 2.18] with (p< 0.001, I
2 =86%) for 6 months, 1.78[1.51, 2.06] with (p< 0.001, I
2 =88%) for 12 months, 1.74[1.56, 1.92] with (p< 0.001) for 18 months, 2.08[1.93, 2.23] with (p< 0.001) for 24 months, 2.70 [2.42, 2.98] with (p< 0.001) for 36 months and 1.74 [1.65, 1.83] with (p< 0.001) for 48 months. There was remarkable reduction in GCSI score with an overall effect size (Z) of 33.60 (p< 0.00001) and a combined MD of 1.84 [1.73,1.95]. However, significant heterogeneity was observed among studies in GCSI; I
2=87%. Gastric retention improvement was evaluated by GES as well. There was a statistically significant difference between the pre-GPOEM and all follow-ups for both GCSI and GES.
Discussion
Our results show that GPOEM is a safe and feasible option for the treatment of RG. We need further studies, especially RCT's, to investigate for further evaluation of our results. This meta-analysis demonstrates the efficacy of G-POEM and the clinical response outcomes are encouraging.
Forest Plot Analysis
Back to 2024 Abstracts
