Back to 2024 Abstracts
TRENDS IN NEOADJUVANT CHEMOTHERAPY UTILIZATION AND TREATMENT SEQUENCING FOR GASTRIC CANCER: ARE WE MAKING PROGRESS?
Alexandra E. Hernandez*, Yujie Wang, Jodie A. Barkin, Alan S. Livingstone, Mehmet Akcin, Cheng-Bang Chen, Laurence R. Sands, Jose M. Martinez, Danny Sleeman, Onur Kutlu
Surgery, University of Miami, Coral Gables, FL
BackgroundOver the past two decades, guidelines for gastric cancer (GC) have shifted. NCCN guidelines recommend chemotherapy for patients with stage IB and beyond. While surgery is an essential part of treatment, perioperative chemotherapy (PCT) and neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NCT) have proven to be superior to surgery with or without adjuvant chemotherapy (ACT). However, NCT is not universally practiced, and the reasons are ill-defined. This study investigates national rates, trends, and factors affecting NCT utilization.
Patients and MethodsUsing the National Cancer Database, patients diagnosed with stage 1B-3 gastric cancer from 2010-2020 were identified. Changes in chemotherapy sequence over time were identified. We performed multivariable regression models to assess factors affecting the receipt of each type of treatment (NCT, PCT, ACT, or none). Factors included age, sex, race, ethnicity, insurance, the Charleson Comorbidity Index, clinical stage, facility type, distance to facility (miles), and case volume.
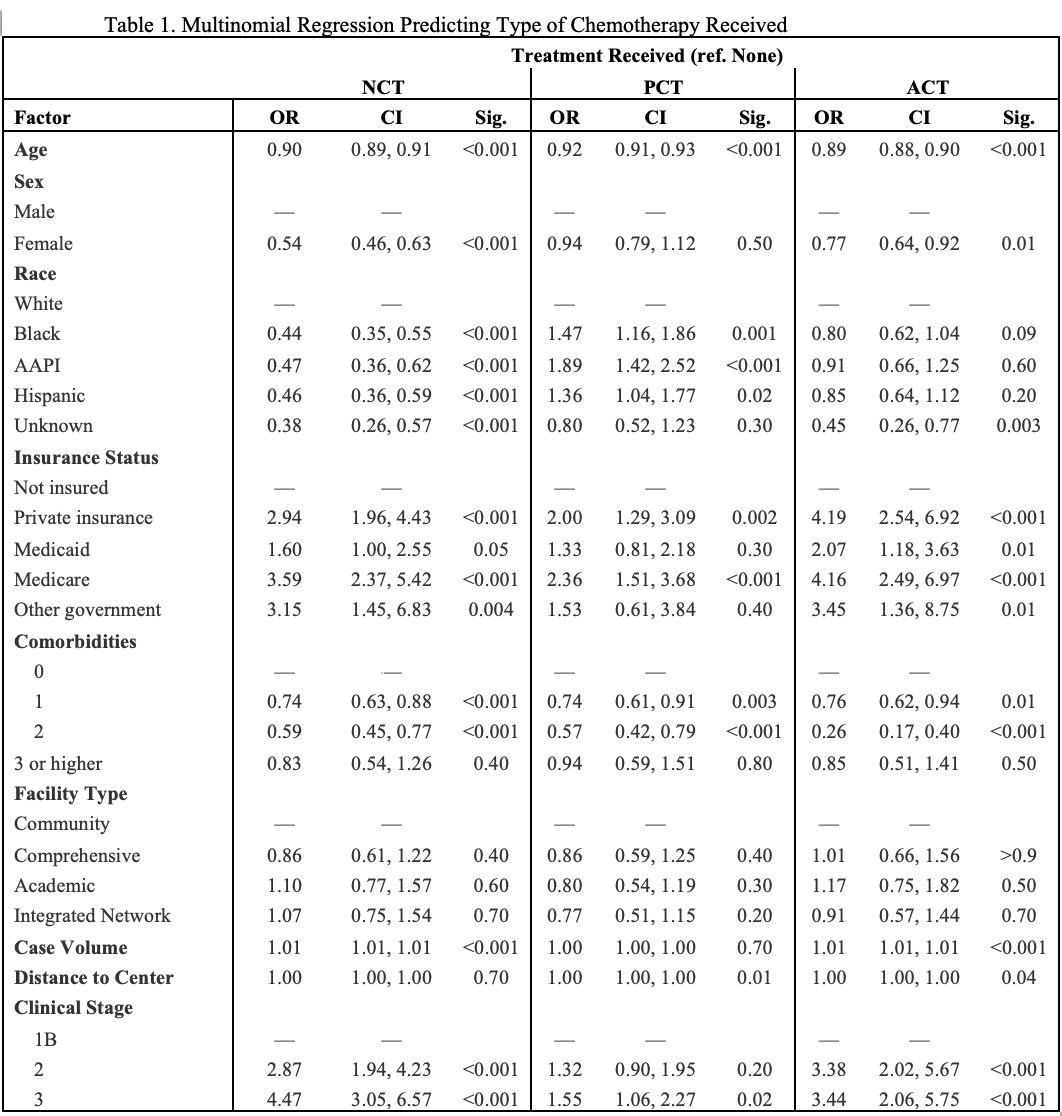
ResultsA total of 10,808 patients met criteria, and 73.9% were female. Mean age of the cohort was 63 (12) years. The majority of the cohort 57.0% (n=6,164) had NCT and NCT utilization increased incrementally over the study period with 68.9% of patients receiving NCT. Factors affecting utilization of NCT were age [OR 0.90 (0.89, 0.91], female sex [OR 0.54 (0.46,0.63)], race [Black OR 0.44 (0.35,0.55); AAPI OR 0.47 (0.36,0.62)], Hispanic ethnicity [OR 0.46 (0.36,0.59)], CCI [1 OR 0.74 (0.63,0.88); 2 0.59 (0.45,0.77)], institutional case volume [OR 1.01 (1.01, 1.01)], stage [II OR 2.87 (1.94,4.23); III OR 4.47 (3.05,6.57)], and insurance status [private OR 2.94 (1.96,4.43); Medicare OR 3.59 (2.37,5.42), other government OR 3.15 (1.45, 6.83)].
ConclusionThis study is the first to define national trends in chemotherapy sequencing in GC in a national cohort. Moreover, our findings highlight the multifaceted determinants of NCT use in GC management, underscoring the need for tailored strategies to optimize access and adherence to evidence-based treatment protocols across diverse patient populations.
Back to 2024 Abstracts
