Back to 2024 Abstracts
COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS OF LAPAROSCOPIC AND ROBOTIC DISTAL PANCREATECTOMY: BALANCING PERIOPERATIVE OUTCOMES AND COSTS
Edward A. Joseph
*1, Bibek Aryal
1, Tyson Barrett
2, Patrick Wagner
1, David Bartlett
1, Sricharan Chalikonda
1, Casey Allen
11Surgical Oncology , Allegheny Health Network, Pittsburgh, PA; 2Highmark Health, Pittsburgh, PA
Introduction The value implications of laparoscopic (LAP) and robotic (ROB) approaches to distal pancreatectomy (DP) remain controversial. We provide a comprehensive analysis of perioperative outcomes and costs associated with LAP and ROB DP.
Methods A retrospective analysis was conducted within our regional health system comprising of patients who underwent ROB or LAP DP 2015 to 2021. We compare perioperative outcomes, 30-day mortality rates, institutional costs and 90-day healthcare utilization between the two surgical groups.
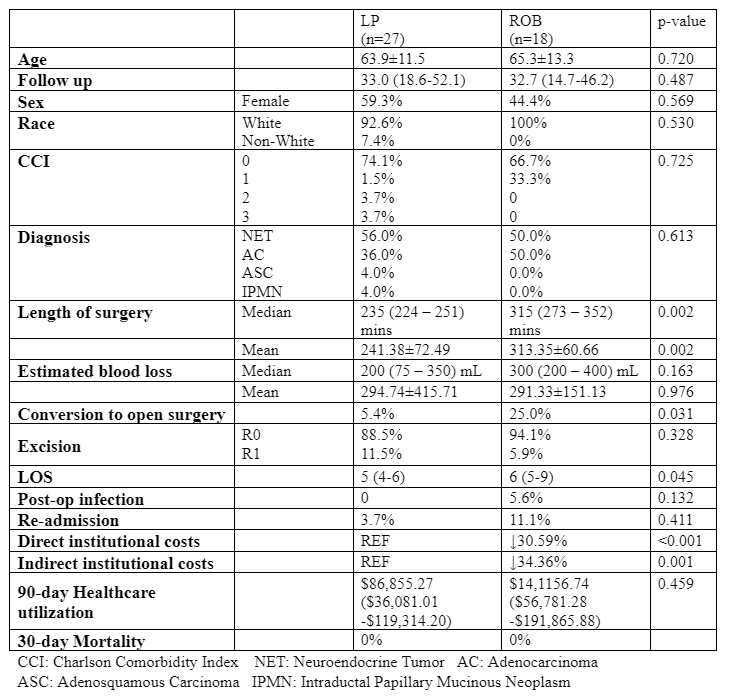
Results Out of 45 patients who underwent DP, 27 underwent LAP and 18 underwent ROB DP. Age was 65.8±10.9 years, with a median follow up time of 30.9 (14.4 – 50.1) months. There was no significant difference in age (63.9±11.5 LAP vs 65.3±13.3 ROB , p=0.720), sex (Female: 59.3% LAP vs 44.4% ROB, p=0.569), race (White: 92.6% 0.338 vs 100.0% ROB, p=0.530), or Charlson comorbidity index (p=0.725) between the two cohorts. Perioperatively, the length of surgery was shorter for patients who underwent the LAP approach [235 (224 – 251) mins vs 315 (273 – 352) mins, p= 0.002]. There was no difference in the estimated blood loss [200 (75 – 350) mL LAP vs 300 (200 – 400) mL ROB, p=0.163] or R0 resection rates (88.5% LAP vs 94.1% ROB, p=0.328) between the two groups. Notably, the duration of hospitalization was lower for patients who underwent the LAP approach [days: 5 (4-6) vs 6 (5-9), p=0.045]. Post-operative infection rates (0.0% LAP vs 5.6% ROB, p=0.132), 30-day readmission rates (3.7% LAP vs 11.1% ROB, p=0.411), and 30-day mortality rates between the two groups (0.0% vs 0.0%, p=1.00). were similar. Direct costs were 30.6% lower, and indirect institutional costs were 34.6% lower for those underwent LAP DP (both p<0.05). The 90-day healthcare utilization was comparable between the two cohorts [$86,855.27 ($36,081.01 - $119,314.20) LAP vs $141,156.74 ($56,781.28 -$191,865.88) ROB, p=0.459].
Outcomes LAP DP was associated with shorter operative time, decreased hospital days, and lower institutional costs in comparison to ROB DP. These findings provide insight into the potential value benefit of LAP over ROB approach for DP.
Back to 2024 Abstracts
