Back to 2024 Abstracts
OUTCOME ANALYSIS OF CAUDATE LOBE AND POSTEROSUPERIOR SEGMENT RESECTION USING ROBOTIC APPROACH: COMPARISON OF LIVER RESECTIONS IN DIFFICULT LOCATIONS
Trevor A. Jones
*, Sharona Ross, Maria Christodoulou, Tara M. Pattilachan, Iswanto Sucandy
Digestive Health Institute, AdventHealth Tampa, Tampa, FL
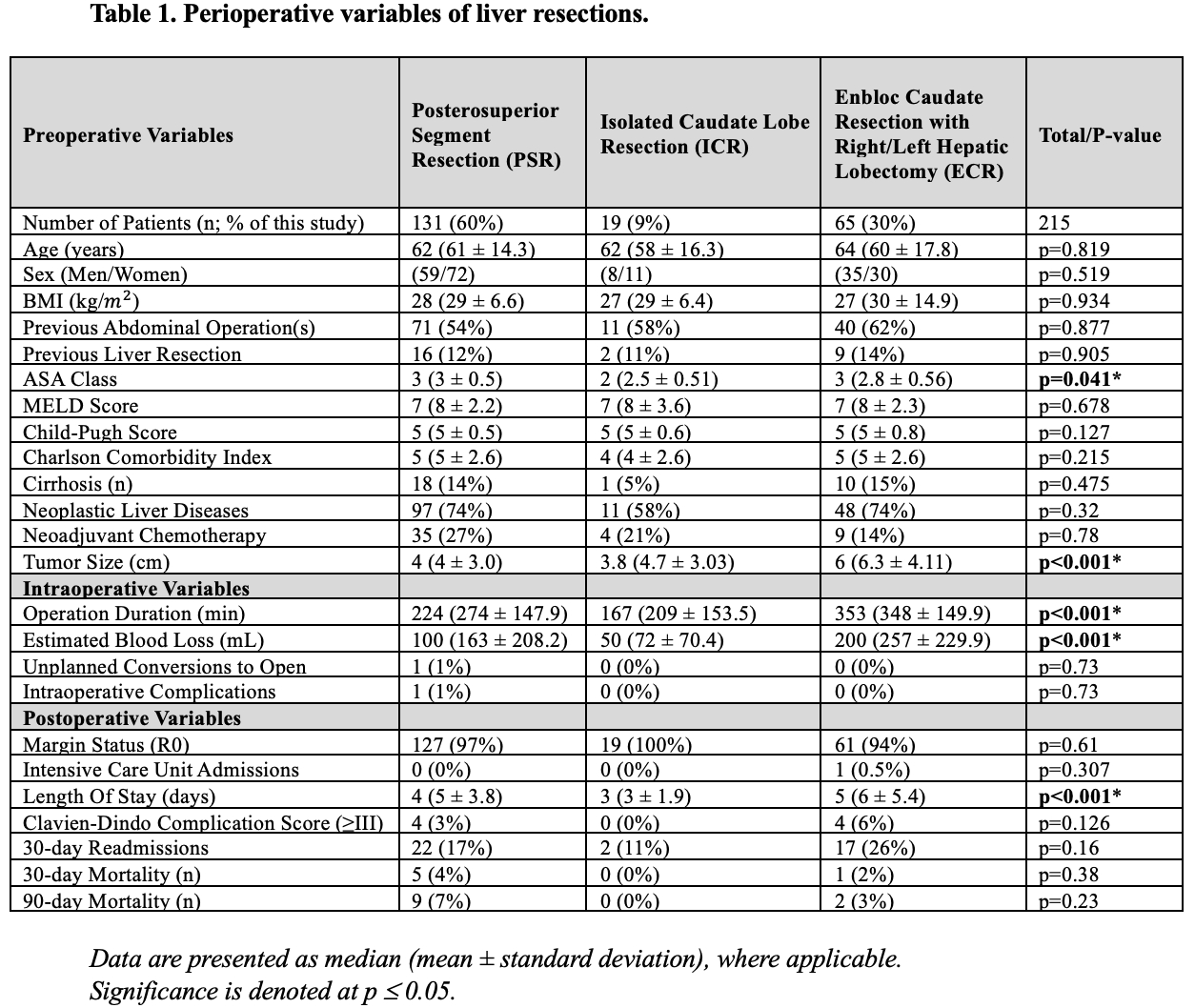
Introduction: Caudate lobectomy (S1) and right posterosuperior resection (S7/8/4A) are technically challenging operations, especially when undertaken using a minimally invasive approach. Many hepatobiliary surgeons are therefore hesitant to offer laparoscopic or robotic approach when these ‘difficult segments' resections are anticipated. While they can provide a curative option for many patients with primary and metastatic liver tumors, published clinical outcome data regarding difficult segment resections are limited. We aimed to analyze the outcomes of isolated caudate resection (ICR), enbloc caudate resection with right/left hepatic lobectomy (ECR), and posterosuperior segment resection (PSR) using robotic approach in our center.
Methods: Following IRB approval, we prospectively followed 500 consecutive patients between 2016 and 2023 who underwent robotic hepatectomy for treatment of hepatobiliary tumors. Posterosuperior segments include segment 7, 8, and 4A. Postoperative complications were graded using Clavien-Dindo classification system. Data are presented as median (mean ± standard deviation).
Results: Of the 500 patients included in this study, 131 (26%) patients underwent PSR, 19 (4%) underwent ICR, and 65 (13%) underwent ECR. Patient demographics were consistent amongst the three resection types. Significant differences were observed between each resection cohort in terms of ASA class, tumor size, estimated blood loss (EBL), operative time, and length of stay (LOS) (all p<0.05). Operative time for ECR was significantly longer and it was associated with increased EBL and LOS, when compared with ICR and PSR, likely a reflection of more extensive operations. The patients who underwent ICR had the shortest operations, lowest EBL, and shortest LOS, when compared with ECR and PSR. Margin status and rate of postoperative complications were similar in all cohorts, regardless of the type of resection.
Conclusions: Robotic isolated and enbloc caudate lobe resection are safe and feasible with similar clinical outcomes as the posterosuperior segment resections. With appropriate expertise, minimally invasive approach to difficult segment resections should not be avoided.
 Data are presented as median (mean ± standard deviation), where applicable. Significance is denoted at p≤0.05.
Data are presented as median (mean ± standard deviation), where applicable. Significance is denoted at p≤0.05.
Back to 2024 Abstracts
