Back to 2024 Abstracts
LONG-TERM PATIENT REPORTED OUTCOMES AFTER MAGNETIC SPHINCTER AUGMENTATION
Ashley Tran
*, Luke R. Putnam, Samantha Mayer, Emma D'Addezio, Tommy Martinez, Caitlin C. Houghton, John C. Lipham
Keck Hospital of USC, Los Angeles, CA
Introduction: Gastroesophageal reflux disease is one of the most common gastrointestinal disorders worldwide. Magnetic sphincter augmentation (MSA, LINX®) is a safe and effective surgical treatment for GERD that obtained FDA approval in 2012. Long-term outcomes of MSA are limited. This study aims to analyze long-term outcomes of MSA in patients followed for a minimum of 5 years.
Methods: Data regarding MSA procedures completed at two institutions from April 2007 through July 2018 was collected from a prospectively maintained database. Information Patient demographics and outcomes including Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease-Health Related Quality of Life (GERD-HRQL) scores, overall satisfaction, and anti-reflux medication usage were included.
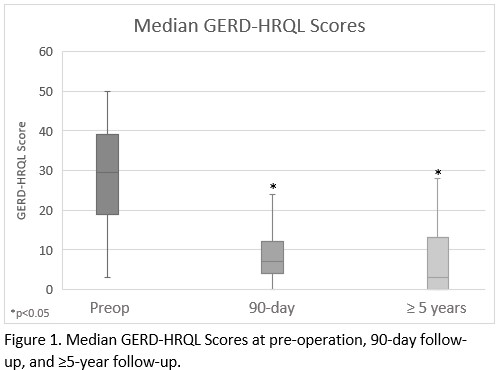
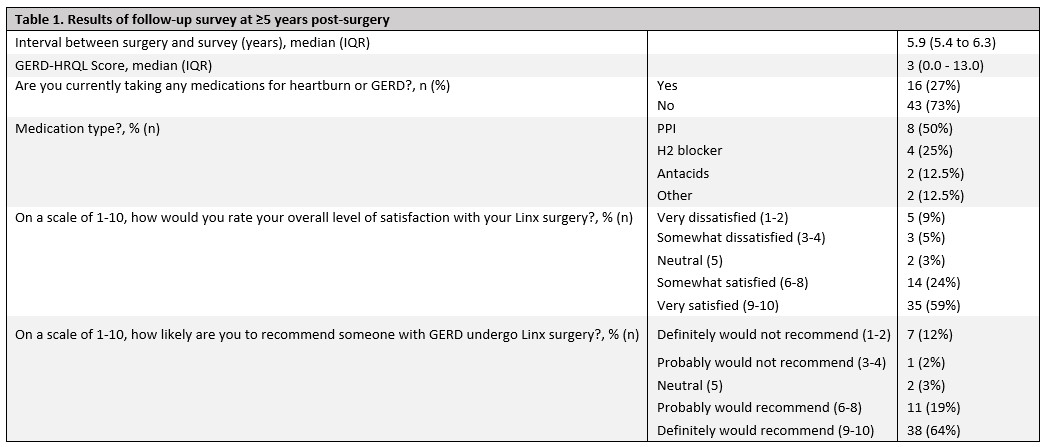
Results: A total of 563 LINX procedures were completed during the analyzed period. The patients were predominantly male (52%) with an average age of 65 ¬± 15 years. There was a significant decrease in median GERD-HRQL scores at 90-days post-MSA compared to pre-operative GERD-HRQL score (7.0 (IQR 4.0 - 12.0) vs 29.5 (IQR 19.0 - 39.0), p<0.001) (Figure 1). Of the 59 patients who completed a recent follow-up survey, the median time since surgery was 5.9 years (IQR 5.4 to 6.3). Only 16 (27%) patients were still taking anti-reflux medications, compared to 88% pre-operatively. At the time of the most recent follow-up survey, the median GERD-HRQL score was 3 (IQR 0.0 - 13.0). There was a significant decrease in median GERD-HRQL scores recorded pre-MSA and at the time of most recent follow-up (29.5 (IQR 19.0 to 39.0) vs 3 (IQR 0.0 to 13.0), p<0.001). Most patients (83%) were ‚Äúvery satisfied‚Ä? or ‚Äúsomewhat satisfied‚Ä? with the results of their LINX procedure and would ‚Äúdefinitely recommend‚Ä? or ‚Äúprobably recommend‚Ä? the MSA procedure to another person (Table 1).
Conclusion: MSA is a durable surgical option for the management of GERD with excellent patient satisfaction.
Back to 2024 Abstracts

