Back to 2024 Abstracts
TRANSORAL SEPTOTOMY VERSUS Z-POEM IN THE TREATMENT OF ZENKER DIVERTICULUM: A CASE-MATCHED COMPARATIVE STUDY
Luca Provenzano
*1, Stefano Siboni
2, Giovanni Capovilla
1, Pamela Milito
2, Cesare Cutrone
3, Matteo Pittacolo
1, Michele Valmasoni
1, Emanuele L. Asti
2, Renato Salvador
11Universita degli Studi di Padova Dipartimento di Scienze Chirurgiche Oncologiche e Gastroenterologiche, Padova, Veneto, Italy; 2IRCCS Policlinico San Donato, San Donato Milanese, Lombardia, Italy; 3Azienda Ospedale Universita Padova, Padova, Veneto, Italy
BACKGROUND: After improving the original technique a few years ago, transoral septotomy has become the favored approach of Zenker Diverticulum (ZD) treatment. Third space endoscopy has recently reached a widespread diffusion in treating different types of diseases in the upper gastro-intestinal tract, and becoming a mini-invasive option also in ZD. The gold-standard treatment of ZD is still debated. We designed a case-matched comparative study with the aim of evaluating whether POEM (Z-POEM) could be as effective as stapler and traction assisted Transoral Septotomy (TS) as first line treatment of Zenker Diverticulum.
METHODS: Consecutive patients undergoing treatment for ZD between 2015-2022 were enrolled in two high-volume centers, one with extensive experience with TS and one with Z-POEM. Patients with recurrent ZD after previous treatments were excluded. Barium-swallow and endoscopy were performed before and after surgery. Symptoms were assessed using a dedicated and detailed ZD questionnaire (Symptom Score, SS). TS and Z-POEM were performed following settled techniques. A total of 124 patients in both centers were thus matched. A control group was generated by matching patients who underwent Z-POEM (treatment group) with those who underwent TS (control group) at the 2 centers in the same time span. Patients were matched for: septum length, follow up time, age, sex. For the purpose of randomization, a one-to-one nearest neighbor approach was used for the selection of patients in the control group. Treatment failure was defined when the post-operative SS was higher than the 10
th percentile of the preoperative SS (i.e.>10) or the need for retreatment.
RESULTS: After matching, 26 patients in the TS group and 26 patients in the Z-POEM group were enrolled. Clinical and demographic data are described in Table 1. The procedures were completed successfully in all patients in both groups, and mortality was null. Four patients in the TS group died during the follow-up, for unrelated causes. TS required a shorter operative time compared to Z-POEM (p<0.001) (Table 2). One leakage was detected in the Z-POEM group while one mucosal tear was detected in the TS group, both treated conservatively with fasting and enteral nutrition. Intra-operative complications were also detected in 3 patients in the Z-POEM group, while none in the TS group (p=0.23). At a median follow-up of 39 months (IQR:21-63) for TS and a median follow-up of 60 months (IQR:51-74) for Z-POEM, a successful outcome was achieved in 96.2% in both groups. Post-operative symptom scores decreased in all patients in both groups.
CONCLUSIONS: This is the first study comparing Z-POEM and TS. Both the minimally invasive treatments are effective for naive Zenker Diverticulum in the mid-term follow-up. TS provides a trend towards a lower rate of intraoperative complications and a shorter operative time.
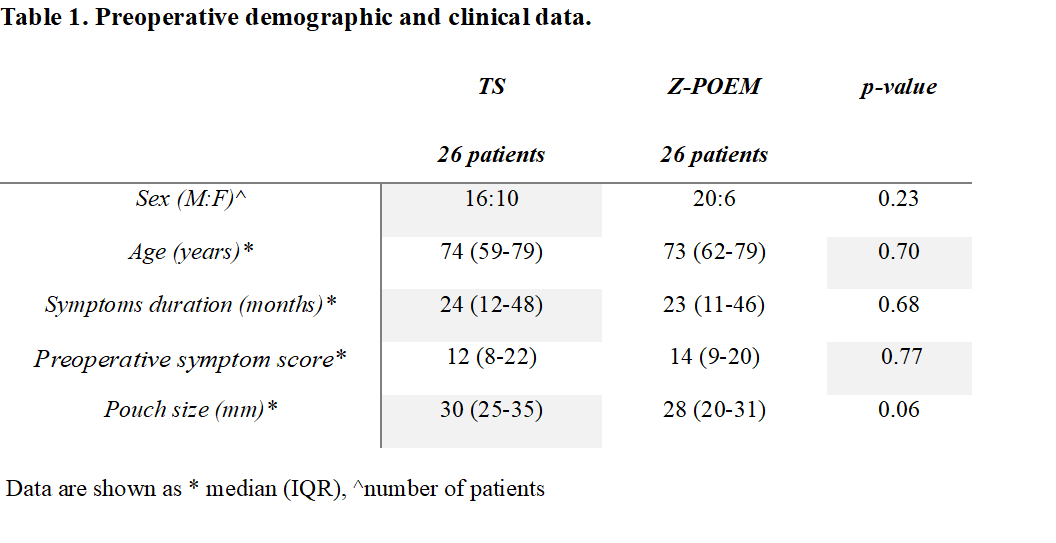 Table 1. Preoperative demographic and clinical data.
Table 1. Preoperative demographic and clinical data.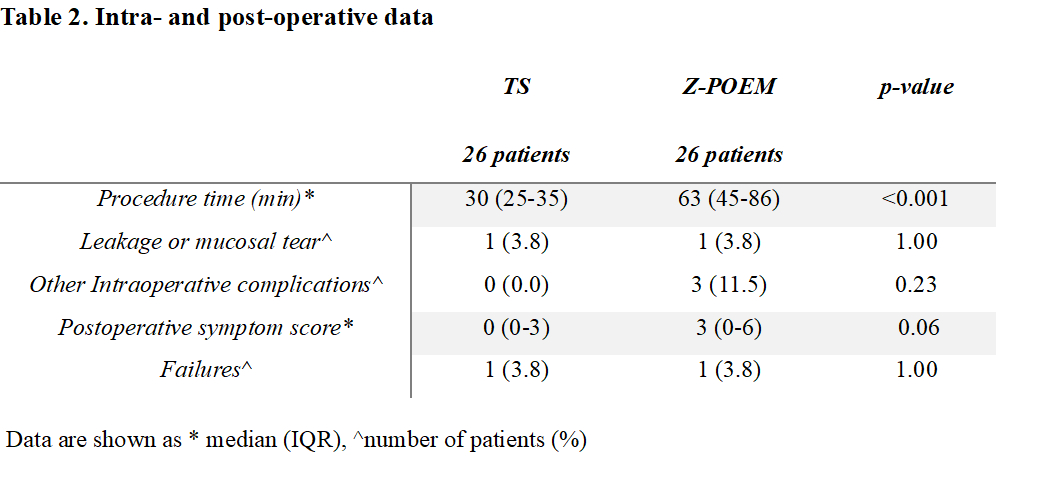 Table 2. Intra- and post-operative data.
Table 2. Intra- and post-operative data.
Back to 2024 Abstracts

