DEVELOPMENT OF AN ACCUMULATION INDEX TO IDENTIFY PANCREATIC SIDE BRANCH INTRADUCTAL PAPILLARY MUCINOUS NEOPLASMS WITH UNDERLYING MALIGNANCY
Menghan Zhao*, Laura R. Prakash, Virginia Hill, Jessica E. Maxwell, Timothy E. Newhook, Naruhiko Ikoma, Ching-Wei D. Tzeng, Jeffrey E. Lee, Matthew Katz, Michael P. Kim
Division of Surgery, The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX
Introduction: High risk stigmata (HRS) and worrisome features (WF) were developed as factors associated with malignancy in side branch intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms (SB-IPMNs) and are used to guide surgical management. How well various combinations of these factors indicate underlying malignancy remains poorly defined.
Methods: We performed a retrospective cohort study of all resected SB-IPMN patients at one institution (January 2000 - March 2020) and compared the individual and summated association between HRS, WFs, and final surgical pathology. Data were analyzed using Chi-square tests, Mann-Whitney U tests, and bivariate and multivariate logistic regressions.
Results: 63 patients with SB-IPMNs underwent resection of whom 38 were female with a median age at diagnosis of 65.3 years. 30/63 patients had non-malignant cysts and 33/63 had malignant disease (high grade dysplasia [HGD] or adenocarcinoma). There were no significant differences between non-malignant and malignant groups in age of diagnosis, age at resection, cyst size at diagnosis, pre-operative cyst size, CA19-9 levels, or number of patients with at least 1 WF. The malignant group had a larger proportion of male patients (p=0.001) and more patients with at least 1 HRS (p=0.047). Overall, 19% of patients had at least one HRS and 84.1% had at least one WF (Table 1).
No patients in the non-malignant group had jaundice, main pancreatic duct (MPD) ?10mm, pancreatitis, change in pancreatic duct (PD) caliber with distal atrophy, or lymphadenopathy (LAD). On bivariate logistic regression, male gender (OR 2.9, p=0.05) and MPD 5-9.9mm (OR 10.3, p=0.004) were individually identified as features predictive for malignancy. On multivariate logistic regression with factors with p?0.2 (gender, MPD 5-9.9mm), only MPD 5-9.9mm remained significant (OR 8.7, p=0.009, Table 1). A 5-point scale was assigned to each HRS and WF weighted based on its significance in predicting malignancy. A score of 5 was given to factors only occurring in malignant patients or p<0.05 on multivariate regression, 4 to factors with p<0.05 on bivariate regression, 3 to factors with p=0.05-0.2, 2 to factors with p=0.2-0.6, and 1 to factors with p=0.6-1 (Table 1). The median accumulated score was 6.5 for non-malignant cysts (range 3-13) and 10 for malignant cysts (range 3-23, p<0.001, Figure 1).
Conclusion: MPD dilation (5-9.9mm) in the setting of SB-IPMNs is a factor consistently associated with underlying malignancy while other solitary HRS or WFs are not strongly associated with malignancy. An accumulation index comprised HRS and WFs, weighted by association with malignancy, may better indicate the underlying presence of pancreatic cancer in SB-IPMNs.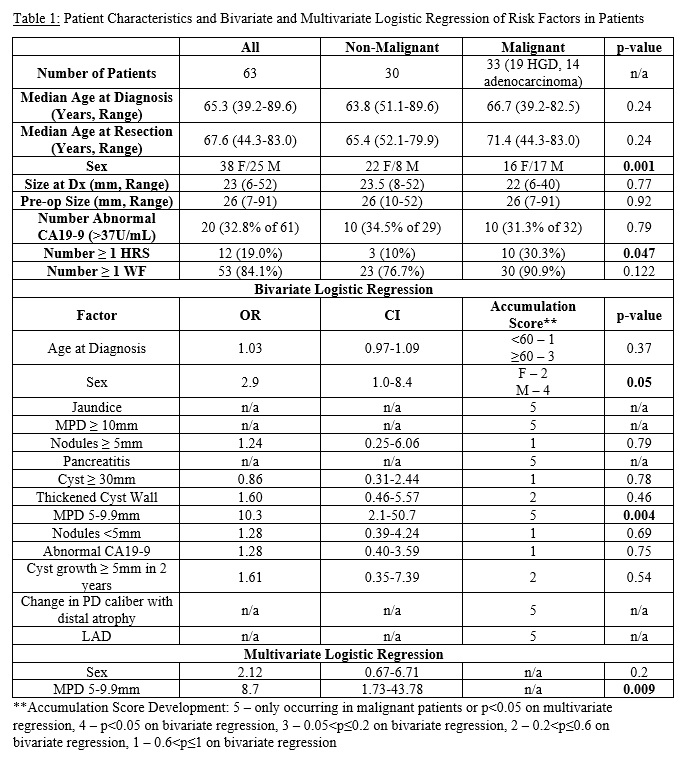
Back to 2022 Abstracts
