THE QUALITY AND CONTENT OF WEB BASED INFORMATION AVAILABLE TO PATIENTS ON HIPEC
Sarah Remer, Tara M. Connelly*, Cillian Clancy, Robert DeBernado, Daniel Joyce, Scott Steele, Michael Valente
Colorectal Surgery, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH
BackgroUND: Patients commonly utilize the internet to obtain medical information. We have noted that patients in our outpatient setting frequently have incomplete or even incorrect information about heated intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC) that they have found on the internet. We aimed to assess both the quality and content of web-based information on HIPEC using validated and novel scoring systems.
METHODS: The keywords "HIPEC" and heated intraperitoneal chemotherapy were entered into the most commonly used internet search engines (Google, Bing, and Yahoo). The first ten websites from each search were analyzed. Website quality using the validated Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA) benchmark criteria and DISERN scoring systems. We created a novel HIPEC-specific score with surgeon experts in the field. This scoring system contains carefully selected details including surgical procedures, chemotherapy types, side effects and outcomes.
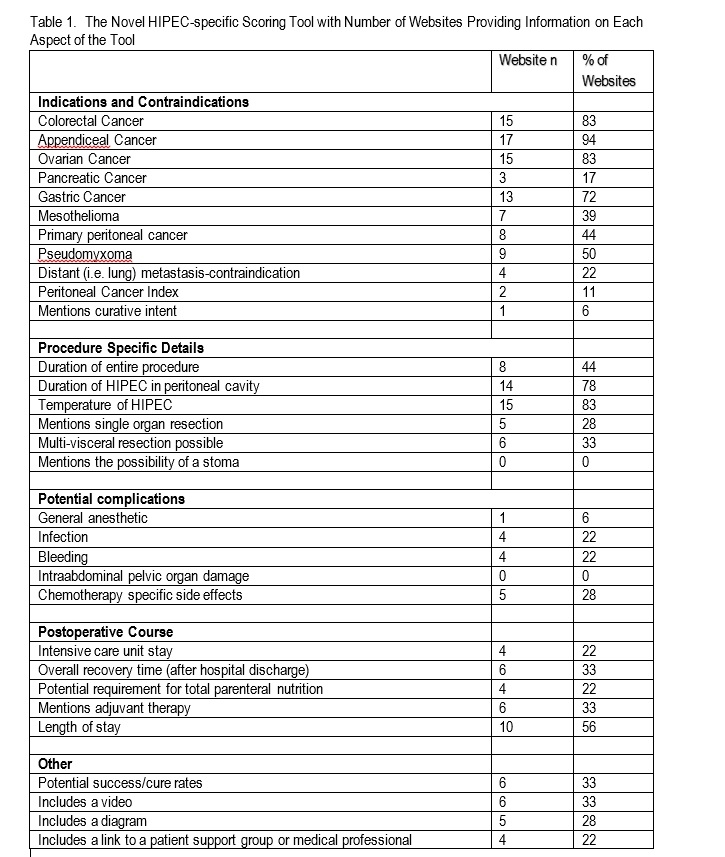
RESULTS: Eighteen unique websites were identified. The majority (78%) were from academic institutions. The mean total DISCERN score for all websites was 41.8 +/- 8.4 (maximum possible points=75). The mean JAMA and HIPEC-specific scores were 1.72 +/- 1.13 (maximum possible score=4) and 11.5 +/- 4.5 (maximum possible score=31), respectively (Figure 1). The lowest JAMA sores were in the category of authorship. 78% of websites omitted author details.. 83% and 78% included the temperature and duration of HIPEC respectively. A video and/or diagram was provided by 50%. Only 39% of websites mentioned complications of HIPEC (Table 1).
CONCLUSIONS: Web-based information on HIPEC is of variable content and quality. None of the websites achieved maximum scores using any of the scoring tools. Less than half of the websites provided any information on possible complications of the procedure. These findings should be highlighted to patients utilizing the internet to obtain information about HIPEC.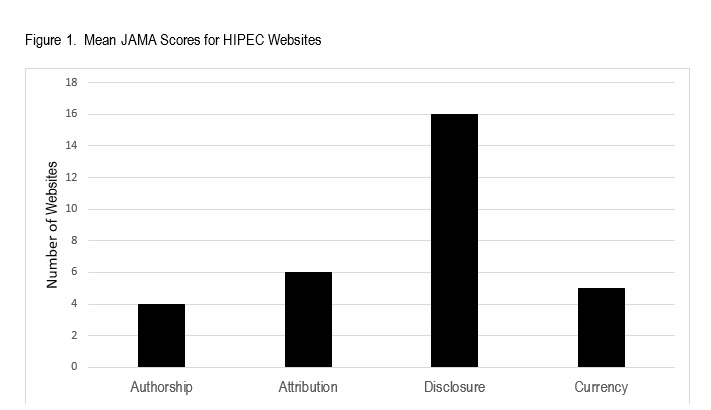
Back to 2022 Abstracts
