INCIDENCE OF AND RISK FACTORS FOR INCISIONAL HERNIA AFTER OPEN HEPATECTOMY FOR COLORECTAL LIVER METASTASES
Timothy J. Vreeland*1,2, Bradford J. Kim1, Yoshikuni Kawaguchi1, Natalia Perez-Arango1, Elena Panettieri1, Timothy E. Newhook1, Donald P. Baumann1, David A. Santos1, Yun Shin Chun1, Ching-Wei D. Tzeng1, Thomas A. Aloia1, Jean-Nicolas Vauthey1
1Surgical Oncology, University of Texas MD Anderson, Houston, TX; 2Brooke Army Medical Center, Fort Sam Houston, TX
OBJECTIVE:
Incisional hernia (IH) is common after major abdominal surgery. However, the incidence after open hepatectomy for cancer has not been described. We analyzed incidence of and risk factors for IH after hepatectomy for colorectal liver metastases (CLM).
METHODS:
Patients who underwent open hepatectomy for CLM at a single institution during 2010-2018 with ?1-year follow-up were retrospectively analyzed. Computed tomography scans were reviewed to identify IH and time from hepatectomy to hernia. Cumulative IH incidence was summarized and compared between groups using log-rank test. Risk factors were examined using Cox regression. Hernia incidence vs body mass index (BMI) was evaluated using generalized additive models.
RESULTS:
Among 502 patients (median follow-up:25.3 months), 1-year and 2-year IH rates were 32.1% and 38.5% respectively. Hernia rates were similar after midline and inverted-L incisions. Independent risk factors identified for IH were surgical-site infection (hazard ratio [HR]:1.6, 95% CI 1.2–2.1, P=0.003), preoperative chemotherapy (HR:2.4, 1.2–4.7, P=0.011), and BMI >25 kg/m2 (HR:1.9, 1.4–2.6, P<0.001). The 2-year IH rate increased with increasing number of risk factors (zero: 8.3%; one: 29.9%; two: 56.1%; three: 63.4%, P<0.001; Figure). Hernia rate increased from 10% to 60% with an increase in BMI from 15 to 40 kg/m2.
CONCLUSIONS:
IH is common after hepatectomy for CLM, particularly in patients who are obese and/or receive preoperative chemotherapy. Surgeons should consider risk-mitigation strategies, including improved fascia closure techniques.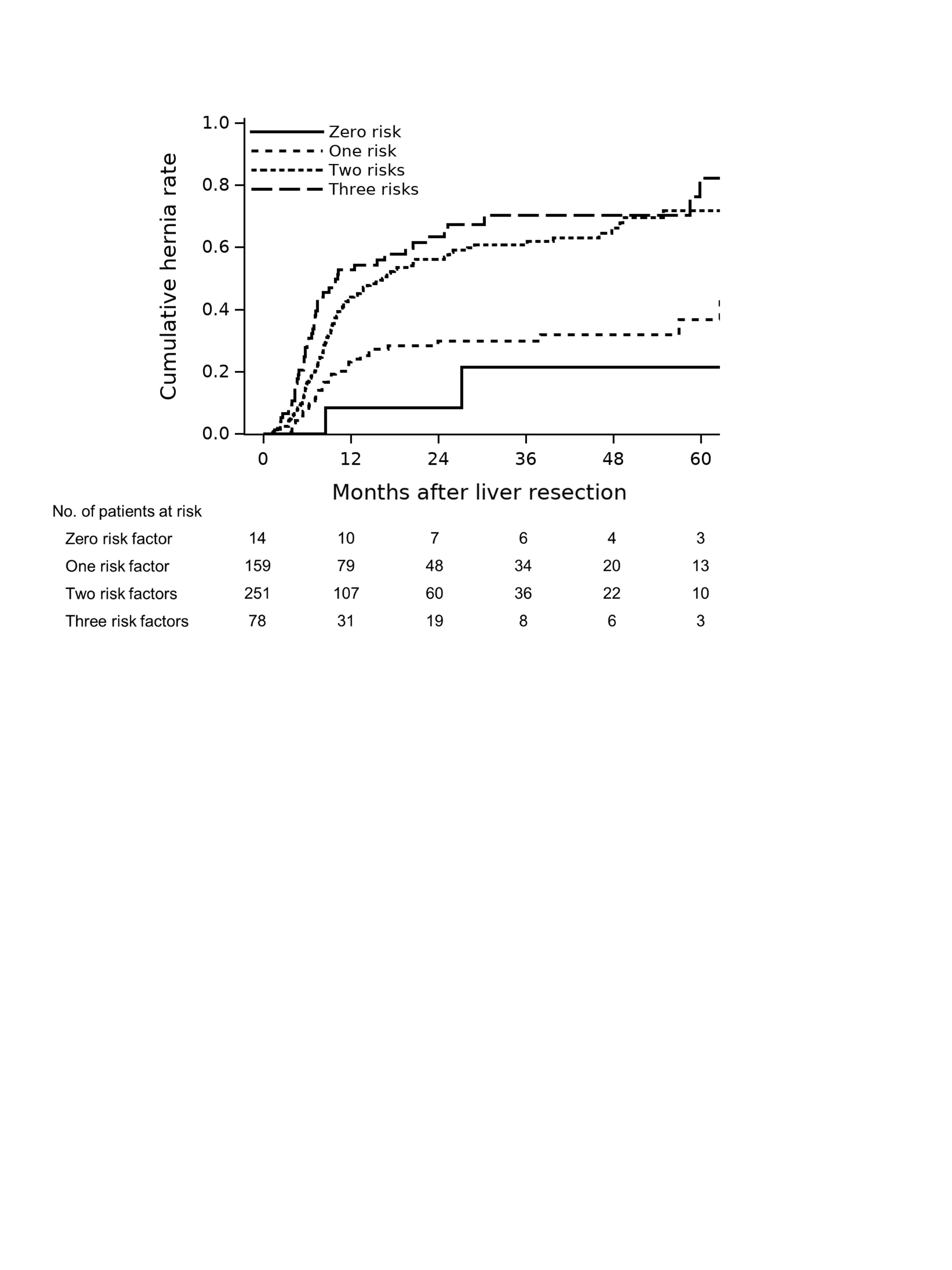
Back to 2022 Abstracts
