|
Back to 2018 Posters
INHIBITOR OF GSK3β IMPEDES THE DEVELOPMENT OF REFLUX-INDUCED ESOPHAGEAL CANCER IN A SURGICAL RAT MODEL
Tomoharu Miyashita*1, Toshinari Minamoto2, Daisuki Matsui1, John W. Harmon3, Tetsuo Ohta1
1Department of Gastroenterological Surgery, Kanazawa University Hospital, Kanazawa, Ishikawa, Japan; 2Division of Translational and Clinical Oncology, Cancer Research Institute, Kanazawa University, Kanazawa, Japan; 3Department of Surgery, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD
Background: Glycogen synthase kinase 3β (GSK3β), a serine/threonine protein kinase, has emerged as a therapeutic target for common chronic diseases including inflammation, immunity and neurodegenerative disorders. GSK3β was recognized as a putative suppressor of cellular neoplastic transformation and tumor development, but emerging evidence suggests that GSK3β promotes various cancers including brain tumors, pancreatic cancer and colon cancer. We evaluated the effectiveness of a GSK3β inhibitor as a chemoprevention agent in a surgical rat reflux model of esophageal cancer.
Materials and Methods: The rat reflux model was created by performing an end-to-side esophagojejunostomy in Sprague Dawley rats. The surgery promoted the reflux of gastro-duodenal contents into the esophagus. GSK3β inhibitor (AR-A014418, Calbiochem, San Diego, CA, USA) was dissolved in 200uL of DMSO. Beginning four weeks post surgery, all animals were administered either 5mg/kg body weight injections of GSK3β inhibitor or equivalent injections of DMSO 3 days per week into the subcutaneous tissue of the back. Animals were sacrificed 40 weeks after surgery and their esophagi were examined.
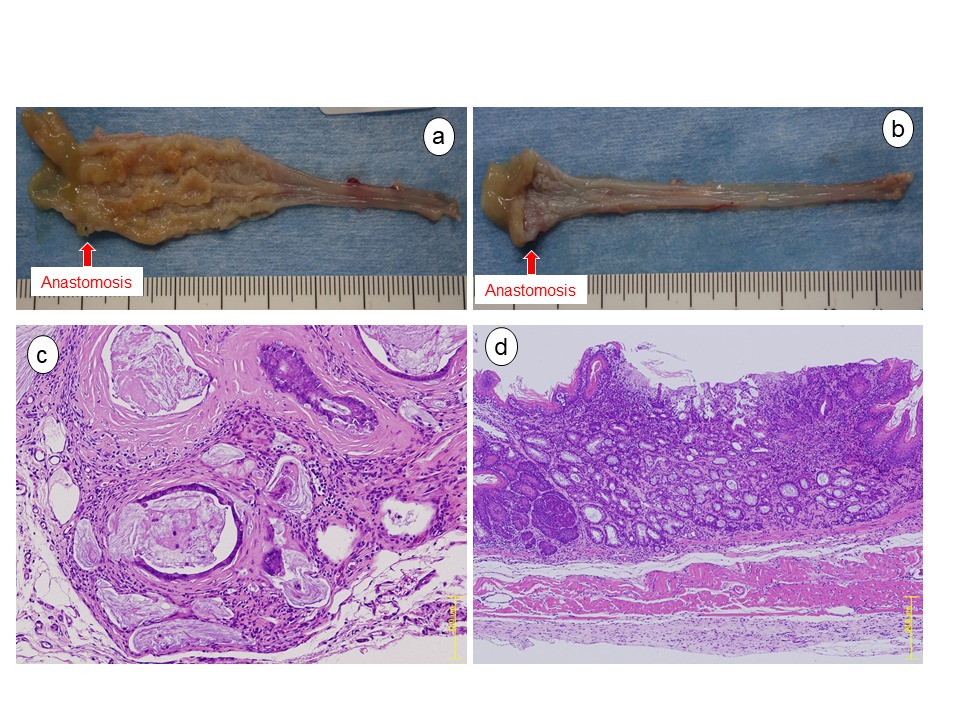
Results: Twenty two rats survived 40 weeks post-surgery and were included in the study. Of these, 12 were included in the control group (Figure 1a), and the remaining 10 received GSK3β inhibitor administration (Figure 1b). 58% (7/12) of the controls developed esophageal cancer (Figure 1c), but animals that received the GSK3β inhibitor did not develop cancer. (0/10) (p=0.005, Chi-squared) (Table 1). Barrett's metaplasia was found in 83% (10/12) of the rats in the control group (Figure 1d). However, only 30% (3/10) of the rats in the GSK3β inhibitor group displayed signs of Barrett's metaplasia, indicating a significant protection of GSK3β inhibitor (p=0.03, Chi-squared). All of the rats in the GSK3β inhibitor and control groups developed proliferative hyperplasia.
Conclusions: GSK3β inhibitor protected against the development of esophageal cancer in a clinically relevant surgical reflux model. Further investigation is required regarding the potential clinical use of GSK3β inhibitor as a chemopreventive agent.
Histological findings
| Histology/Group | Control | GSK3β inhibitor | p value | | Proliferative hyperplasia | 12 (100%) | 10 (100%) | n.s. | | Squamous dysplasia | 9 (75%) | 1 (10%) | p=0.004 | | Barrett's metaplasia | 10 (83%) | 3 (30%) | p=0.03 | | Carcinoma | 7 (58%) | 0 (0%) | p=0.005 |
Back to 2018 Posters
|

