|
Back to 2018 Posters
LEUKOCYTOSIS AFTER DISTAL PANCREATECTOMY AND SPLENECTOMY (DPS): A MARKER OF MAJOR COMPLICATIONS?
Stephen N. Quigley*1, Thomas K. Maatman1, Trevor Crafts2, James Butler1, Nicholas J. Zyromski1, Eugene P. Ceppa1, Attila Nakeeb1, C. Max Schmidt1, Michael G. House1
1Surgery, Indiana University, Indianpolis, IN; 2Surgery, Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, OR
Background:
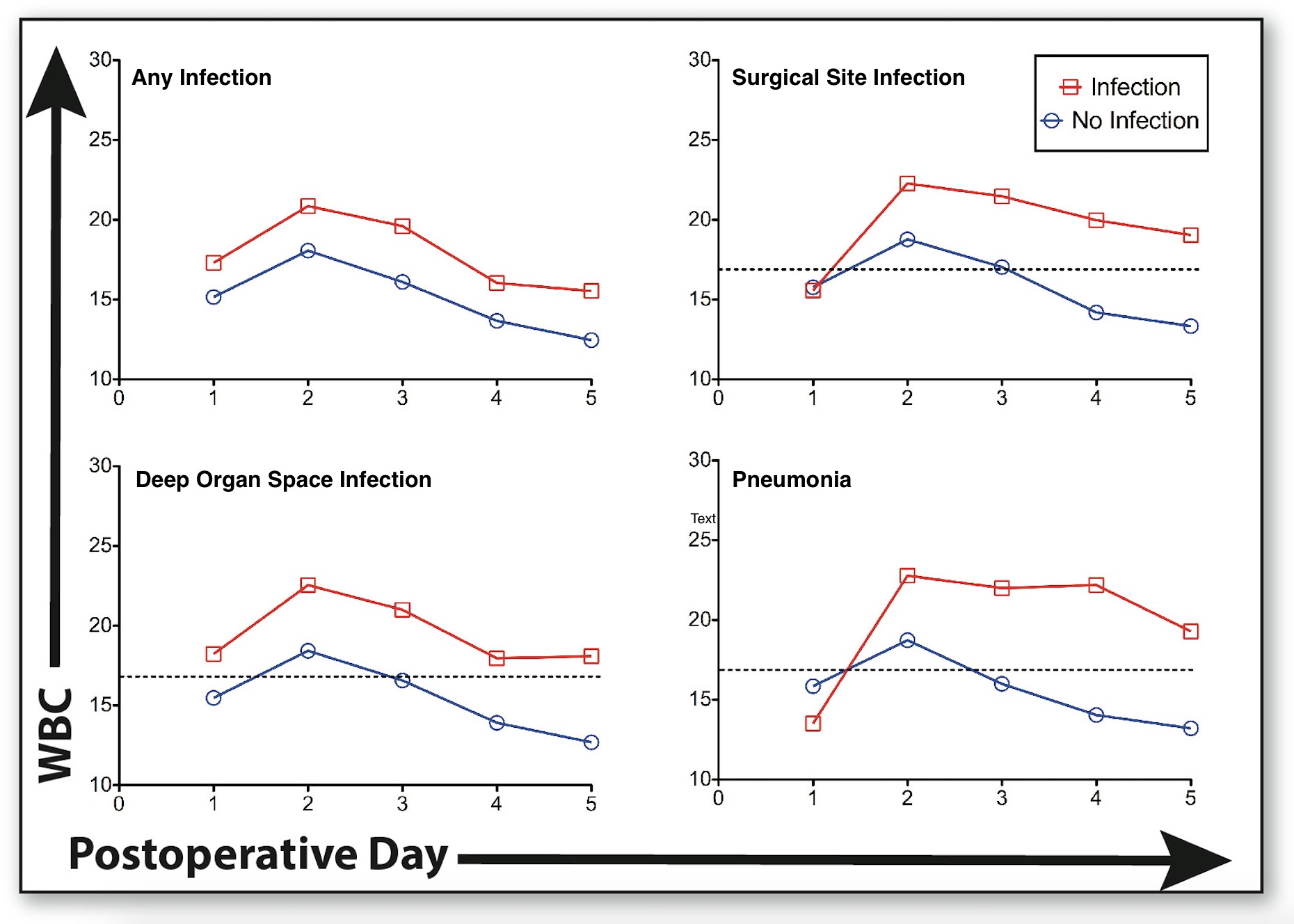
Post-splenectomy leukocytosis is a normal physiologic response, but has been prospectively validated as a reliable marker for postoperative complications. The aim of this study was to analyze the associations between trends in postoperative leukocytosis and infectious complications after distal pancreatectomy with splenectomy.
Methods:
Between January 2013 and December 2015, patients undergoing distal pancreatectomy with splenectomy (DPS) for primary pancreatic diseases were analyzed from a single institution database. Independent t-test were performed to analyze the bivariate relationships between the postoperative leukocytosis and short-term postoperative outcomes including infectious complications, pancreatic fistula, and 30-day hospital re-admission.
Results:
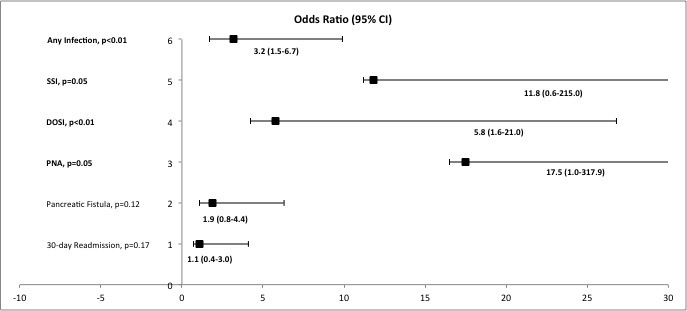
DPS was performed in 158 patients, 106 (67%) open and 52 (33%) laparoscopic or robotic. Median age of all patients was 57 years (range 22-89). Median BMI was 28 kg/m2 (range 15-54), and 30% had preoperative diabetes mellitus. Patients developing postoperative infectious complications had significantly higher WBC counts beginning on postoperative day (POD) 2. A similar pattern was identified for superficial surgical site infection (SSI) beginning POD 4, deep organ-space infections (DOSI) beginning POD 2, and pneumonia (PNA) beginning POD 4; Figure 1. Leukocytosis above 16,000 cells/mcL on or after POD3 was associated with SSI, DOSI, and PNA. WBC count did not correlate with UTI, post-operative pancreatic fistula, or 30-day readmission.
Conclusion
A leukcocytosis of 16,000 cells/mcL or greater on or after post-operative day three following distal pancreatectomy with splenectomy should raise awareness for postoperative infectious complications.
Back to 2018 Posters
|


