|
Back to 2018 Program and Abstracts
NATIONAL TRENDS OF POUCH CREATION AND EXCISION OVER A DECADE: A STUDY FROM NSQIP DATABASE
H. Hande Aydinli*1, Ozgen Isik2, Michael Grieco1, Hasan T. Kirat1, Feza H. Remzi1
1Department of Surgery, New York University, New York, NY; 2Department of Surgery, Uludag University Faculty of Medicine, Bursa, Turkey
Background: There are limited data on the postoperative morbidity and mortality associated with pouch excision. Much of the literature on pouch excision is from high volume centers whose outcomes may not reflect the national experience. The aim of this study is to evaluate the trends and outcomes after pouch excision from a national database.
Methods: American College of Surgeons National Surgical Quality Improvement Program (ACS-NSQIP) database (2005-2015) was queried for all patients who underwent ileal pouch anal anastomosis (IPAA) creation and pouch excision by using CPT codes. Demographics, comorbidities, operative and postoperative outcomes were compared between two groups. Groups were compared using χ2 or Fisher exact
tests for categorical and Wilcoxon rank-sum test for quantitative data. Multivariate logistic regression analysis was
conducted.
Results: A total of 6,685 patients met the inclusion criteria. Five percent of the patients (N= 336) underwent pouch excision with a mean age of 47 (standard deviation ± 14). Patients who underwent pouch excision was older (47.3± 14 vs. 44.1± 15 years, p<0.01) with a lower body mass index (24.6± 5.1 vs. 26.7± 5.8 kg/m2, p<0.01). Female gender (52.9% vs. 43.3%, p<0.01), smoking (15.1% vs. 11.6%, p<0.01), wound infection (5.6% vs. 08%, p< 0.01), preoperative sepsis (3.6% vs. 1.8%, p=002), an American Society of Anaesthesiologists score of III-IV (42.2% vs. 31.1%, p<0.01), and anemia (45.7% vs. 37%, p<0.01) were more common in excision group whereas diagnosis of hypertension (20.2% vs. 11.9%, p<0.01) and steroid use (27.4% vs.19.9%, p<0.01) in IPAA creation group. Change of the rates of pouch excision and creation in a year over a decade is summarized in figure (p<0.01). Thirty percent of the patients (N= 2019) had at least one postoperative complication (Excision: 42.2% vs. Creation: 29.5, p<0.01). Length of stay was 2 days longer in pouch excision group when compared to creation (p<0.01).
Conclusions: Pouch excision is a major procedure with longer length of stay and higher postoperative short-term morbidity when compared to pouch creation. Although there are many confounding variables, the reduction in rate of pouch excision might be secondary to improving operative skills. More centralized IBD surgery practice might optimize the outcomes.
Comparison of patient characteristics and perioperative outcomes between the groups.
| | Pouch Creation
N= 6349 (95) | Pouch Excision
N= 336 (5) | p-value | | Gender, female | 2753 (43.3) | 178 (52.9) | <0.01 | | Age, years ¥ | 44.1± 15 | 47.3± 14 | <0.01 | | BMI, kg/m2 | 26.7± 5.8 | 24.6± 5.1 | <0.01 | | Diabetes Mellitus | 434 (6.8) | 20 (5.9) | 0.50 | | Functional status, Dependent | 58 (0.9) | 7 (2.1) | 0.06 | | COPD | 91 (1.4) | 3 (0.8) | 0.40 | | Hypertension | 1288 (20.2) | 40 (11.9) | <0.01 | | Steroid use | 1743 (27.4) | 67 (19.9) | <0.01 | | Weight loss | 287 (4.5) | 19 (5.6) | 0.30 | | Preoperative wound infection | 51 (0.8) | 19 (5.6) | <0.01 | | Preoperative sepsis | 115 (1.8) | 12 (3.6) | 0.02 | | ASA class III-IV | 1997 (31.1) | 142 (42.2) | <0.01 | | Wound class 3-4 | 985 (15.5) | 116 (34.5) | <0.01 | | Anemia, severe | 256 (4.4) | 23 (7.0) | <0.01 | | Hypoalbuminemia <3 gr/dL | 400 (10.3) | 30 (13.3) | 0.15 | | Operative time, minutes ¥ | 266.2± 110 | 254.4± 113 | 0.09 | | Length of stay, days ¥ | 7.9± 6 | 9.9± 10 | <0.01 | | Mortality | 34 (0.5) | 3 (0.9) | 0.38 | | Morbidity | 1877 (29.5) | 142 (42.2) | <0.01 | | Superficial SSI | 419 (6.6) | 32 (9.5) | 0.03 | | Deep SSI | 114 (1.8) | 13 (3.9) | <0.01 | | Organ space SSI | 521 (8.2) | 34 (10.1) | 0.20 | | Transfusion | 435 (6.9) | 50 (14.9) | <0.01 | | DVT | 169 (2.7) | 3 (0.9) | 0.04 | | Reoperation | 430 (6.8) | 20 (6) | 0.50 | | Readmission | 431 (10.9) | 19 (9.8) | 0.40 | | UTI | 278 (4.3) | 19 (5.6) | 0.20 | | Sepsis | 423 (6.7) | 31 (9.2) | 0.06 | | Pneumonia | 78 (1.2) | 8 (2.3) | 0.06 |
Values are expressed as absolute numbers (percentages) unless indicated otherwise. ¥-Values are expressed as mean ± standard deviation. COPD : chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. ASA: American Society of Anesthesiologists, SSI: Surgical site infection, DVT: deep venous thrombosis, UTI: urinary tract infection. Missing data for readmission in 2545 patients. 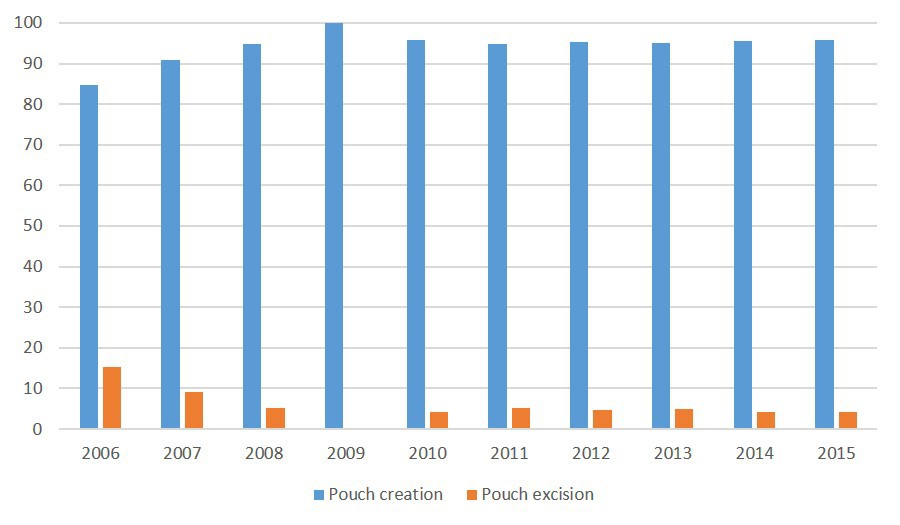 Rates of pouch creation and excision through years.
Back to 2018 Program and Abstracts
|

