|
Back to 2018 Program and Abstracts
THE LONG TERM EFFECT OF METABOLIC PROFILE AND MICROBIOTA STATUS IN PATIENTS AFTER SUBTOTAL GASTRECTOMY
Xi Hsuan Lin*, Jiing-Chyuan Luo
Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Taipei Veterans General Hospital, Taipei, Taiwan
OBJECTIVES: Recent studies indicate that gut microbiota may mediate some of the beneficial effects of bariatric surgery. However, information about long-term effect of subtotal gastrectomy on gut microbiota modifications with subsequent metabolic profiles are limited. We aimed to investigate and compare long-term effects of metabolic profiles and microbiota status in early gastric cancer patients receiving curative subtotal gastrectomy to the controls.
METHODS: In this cross-sectional study, we analyzed type II diabetes mellitus (DM) and metabolic syndrome (MS) occurrence in two groups: 111 patients after curative subtotal gastrectomy with Billroth II anastomosis (BII) and Roux-en-Y gastrojejuno anastomosis (RYGJ) and 344 age-sex matched controls. Fecal samples from those with BII, RYGJ, and controls were analyzed by next-generation sequencing method.
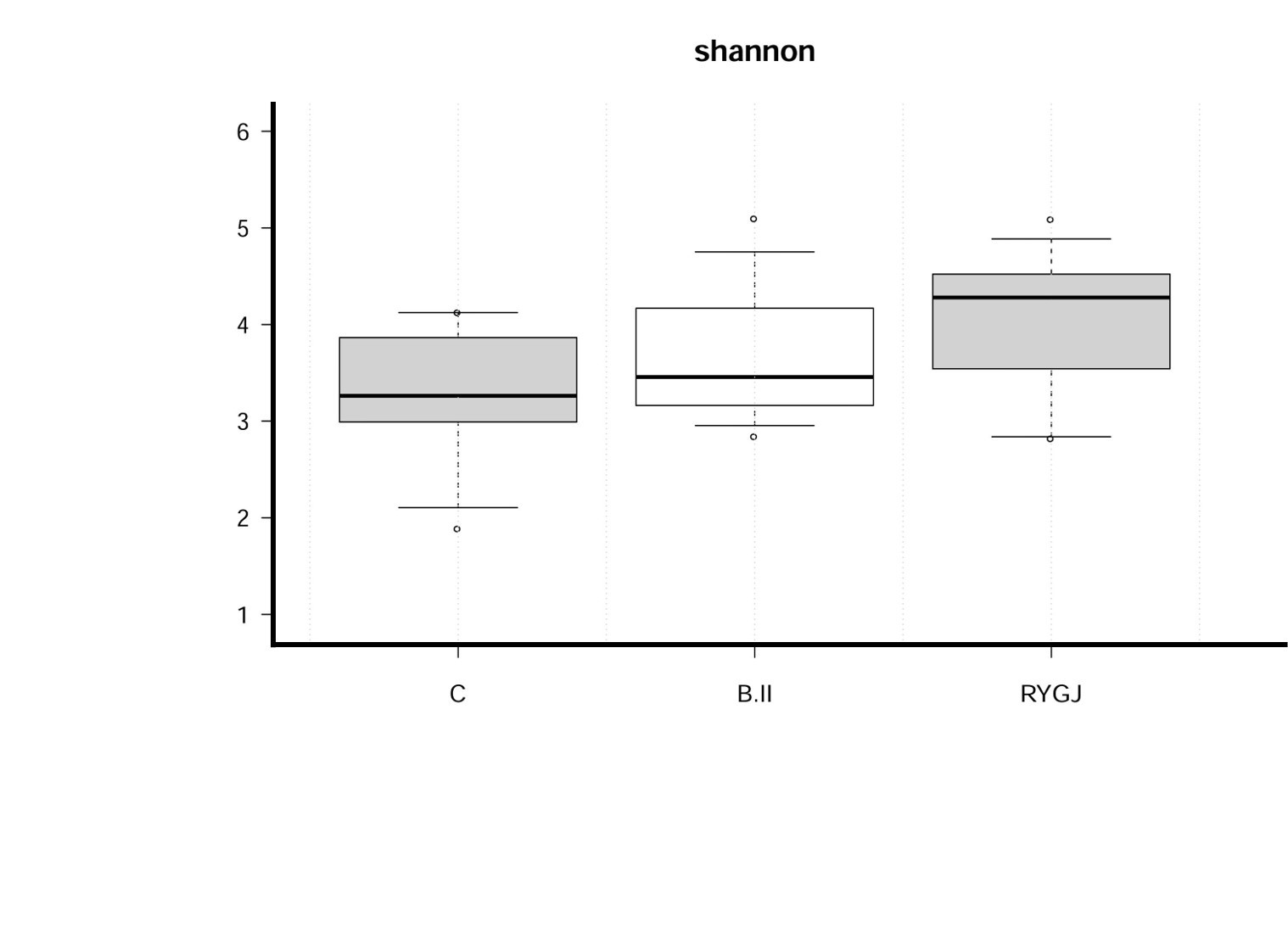
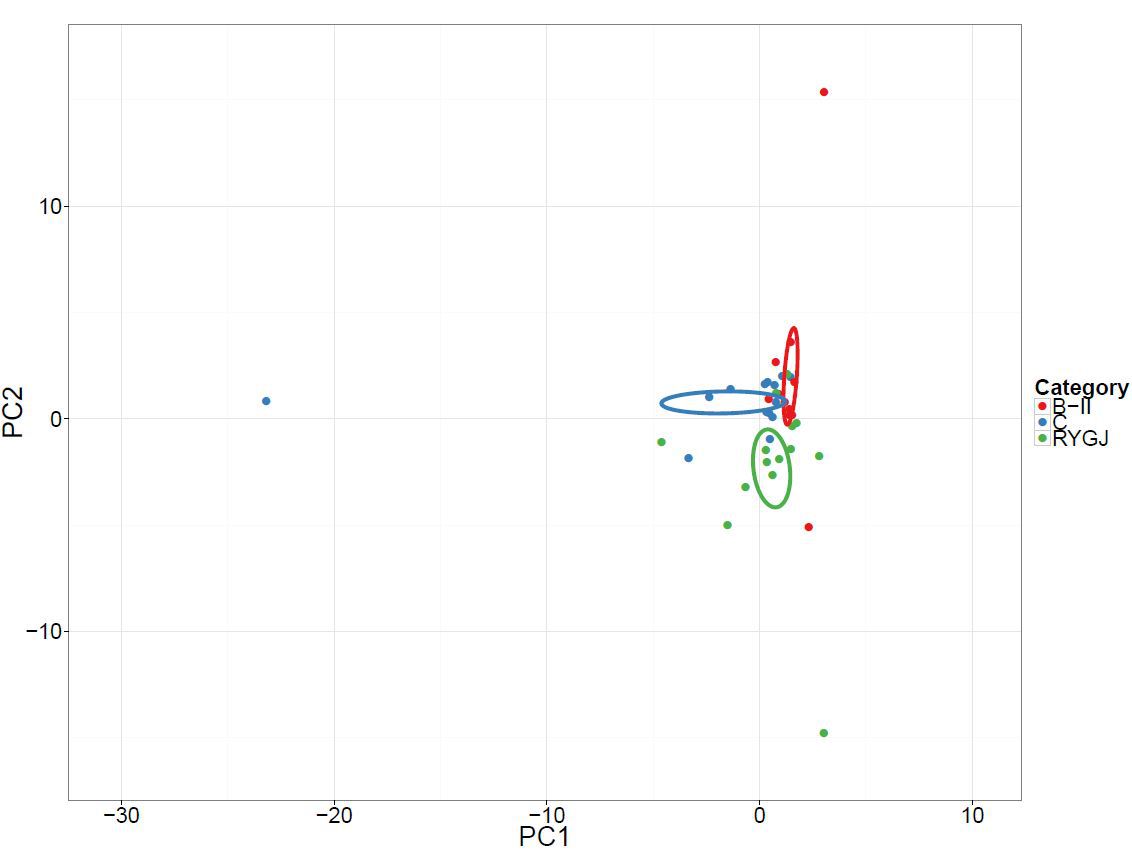
RESULTS: MS and DM occurrences were significantly lower in patients after subtotal gastrectomy with RYGJ than in controls over the long term (>5 years) follow-up (P <0.05). The richness and diversity of gut microbiota significantly increased after subtotal gastrectomy with RYGJ (P <0.05). Compared with the control group, the principal component analysis revealed significant differences in bacterial genera abundance after subtotal gastrectomy with BII and RYGJ (P <0.001). Oscillospira, Prevotella, Coprococcus, Veillonella, Clostridium, Desulfovibrio, Anaerosinus, Slackia, Oxalobacter, Victivallis, Sporobacter, and Campylobacter shared more abundant roles both in the RYGJ group and BII groups.
CONCLUSIONS: Early gastric cancer patients after subtotal gastrectomy with RYGJ had a lower occurrence of MS and type II DM than the controls during long-term follow-up. In parallel with the metabolic improvements, gut microbial richness and diversity also significantly increased after subtotal gastrectomy with RYGJ.
Back to 2018 Program and Abstracts
|


