|
Back to 2017 Posters
ULTRASOUND GUIDED LIVER RESECTION APPROACH FOR MULTIPLE BILOBAR COLORECTAL LIVER METASTASIS WITH COMPLEX PRESENTATION: TECHNICAL ASPECTS AND FLOW CHART
Matteo Maria Cimino*, Luca Vigano', Fabio Procopio, Matteo Donadon, Guido Torzilli
Department of Surgery Division of Hepatobiliary & General Surgery, Humanitas Research Hospital & Humanitas University, Rozzano, MI, Italy
Background Data: multiple bilobar colorectal liver metastases (CRLM) with main vascular intrahepatic contacts is one of the most challenging disease for an hepatobiliary team. Complete clearance of the disease is often not possible due to the small volume of the future remnant liver (FRL). Several strategies have been proposed to overcome this problem (e.g. Staged procedures, or intraoperative radiofrequency ablation). Our group proposed the complete removal of all lesions in a single stage (one stage hepatectomy, OSH) thank to the extensive use of intraoperative ultrasonography. The aim of the study is to analyze surgical strategy applied in this complex CRLM presentations and devise a flow chart according to patients characteristics.
Methods: 457 consecutive patients undergoing first liver resection (LR) for CLM between 2002 and 2015 were considered. Patients carrier of multiple (≥4) CLM with intrahepatic major vascular contact were included.
Results: 164 patients were analyzed. OSH was possible in 155 (95%) patients including 12 SERPS, 1 transversal hepatectomy, 2 mini-mesohepatectomies, 6 liver tunnels. 9 Patients underwent two stage hepatectomy (TSH). One hundred and three patients (63%) had a monolateral main intravascular contacts whereas 61 patients (37%) had bilateral vascular contacts.
The median number of resected CRLMs were 7 ( range 4-48) and 63 (38%) patients had >10 nodules. Seventy patients (42%) had a main intrahepatic vascular detachment or reconstruction.10 patients of the OSH group underwent major hepatectomy associated to limited resections. Reasons to perform major hepatectomies for OSH group were the following:
- infiltration of umbilical portion (5/10) for left hepatectomy.
- uncountable, disappearing, huge lesions (4/10, 40%) or 360° infiltration of the right portal branch (1/10, 10%) for right hepatectomy.
Twenty four patients have concomitant extrahepatic disease. Twelve patients have lung deposits (12/24, 50%).
Mortality and morbidity rates were 1,2% and 36%. Five-year overall survival (OS) was 32% (median overall survival 40,2 months). Disease free survival at 5 years was 17% (median 12 months). TSH patients compared to OSH showed no difference except for more cycles of chemotherapy (>6 cycles), higher rate of patients with more than 10 lesions, associated surgical resection (colon resections), more vascular infiltration and more parenchymal R1. According to these findings we devised a flow chart for multiple bilobar CRLM treatment. At univariate analysis re-resection was the only positive prognostic factors for OS (p< 0,001).
Conclusions: OSH for CRLMs is safe and effective. According to the evidence that re-resection is a protective factor for OS, parenchymal spare resections must be attempted whenever possible to increase FRL.TSH must be reserved for a selected number of patients.
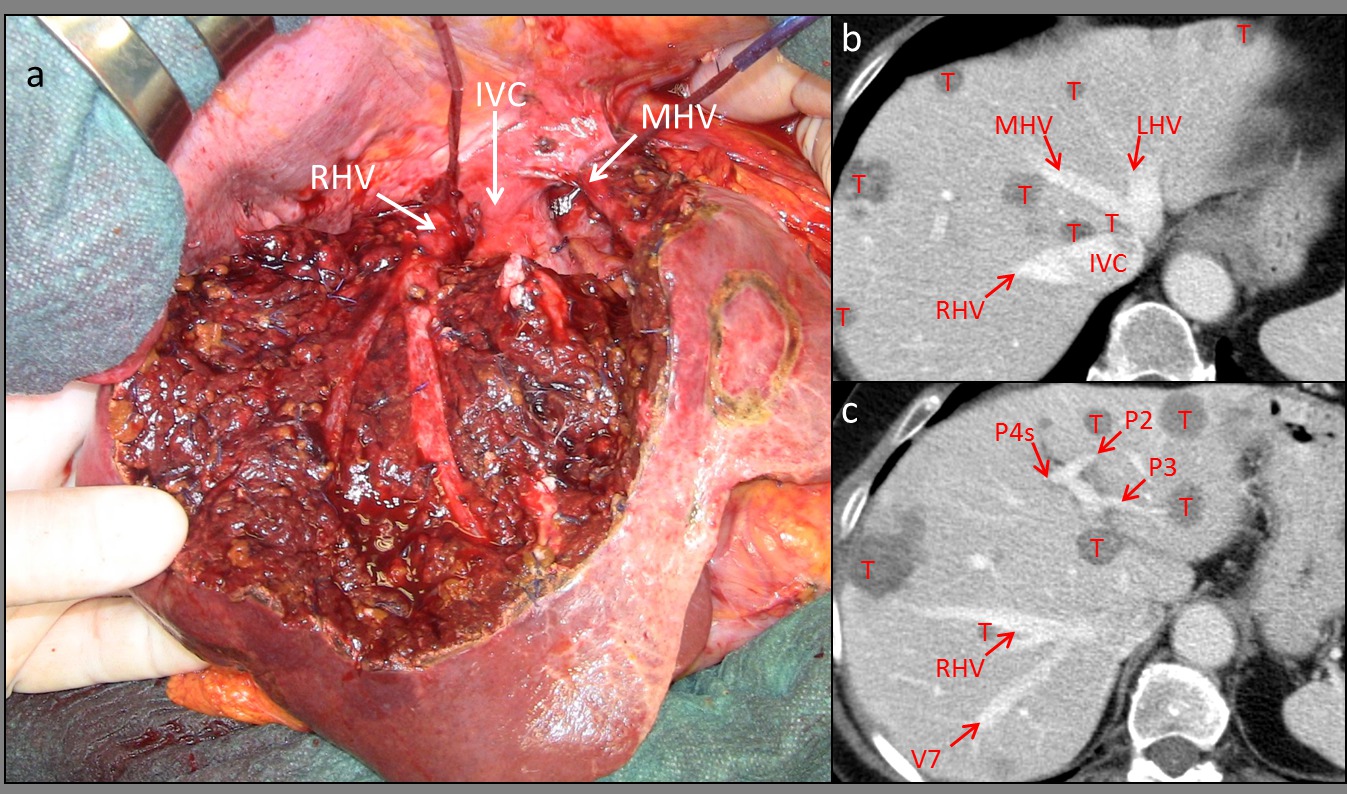
Fig 1. An example of parenchimal spare resection: liver tunnel associated with multiple liver resection in a 71 year old patient with multiple bilobar CRLM. a) intraoperative picture liver tunnel with the exposure on the cut surface of the RHV and MHV. b-c) preoperative CT scan. Abbreviations. RHV: right hepatic vein IVC: inferior vena cava, MHV: middle hepatic vein, LHV: left hepatic vein, V7: vein draining segment 7 tributary of the RHV, P4s: portal pedicle of segment 4, P2: portal pedicle segment 2, P3: portal pedicle segment 3
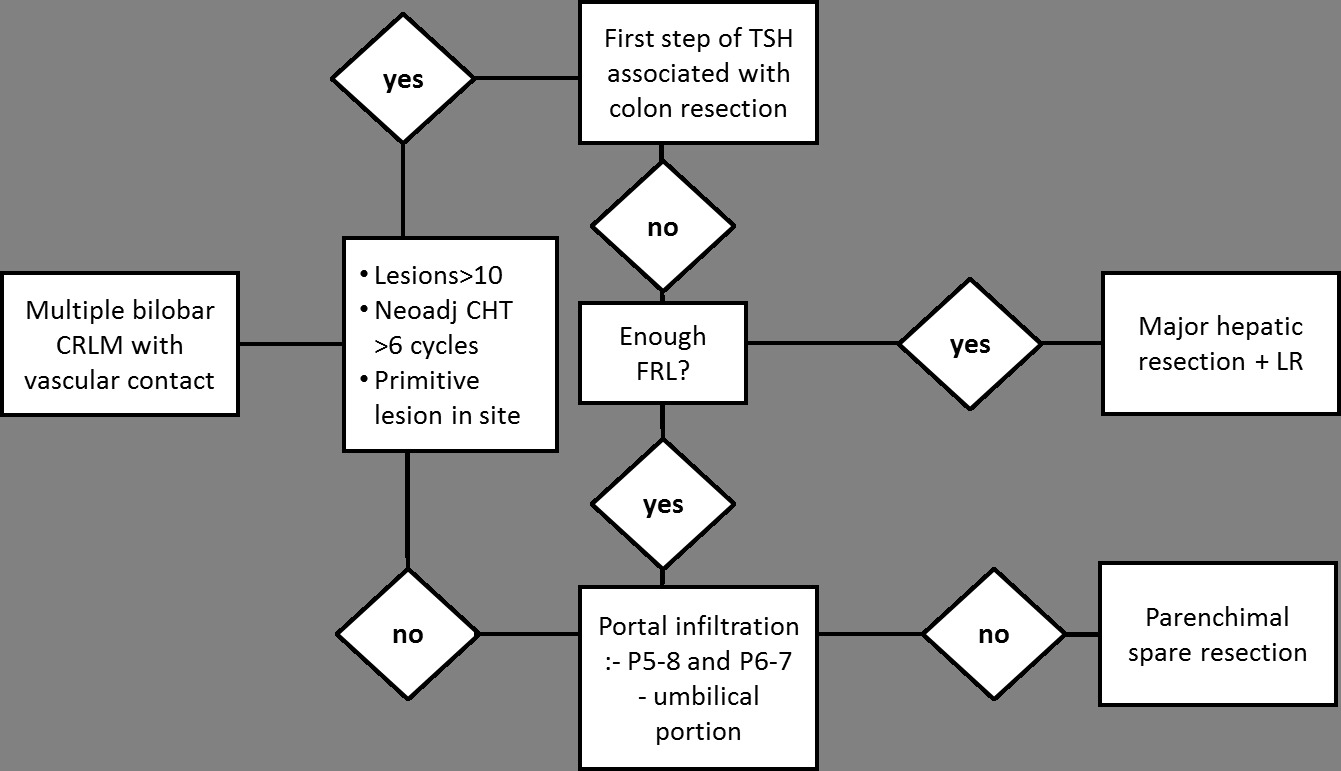
Fig 2. Flow chart of surgical treatment of multiple bilobar CRLM with main intrahepatic vascular contact. CRLM: colorectal liver metastases CHT: chemotherapy, P5-8: right anterior portal branch, P6-7: right posterior portal branch, FRL: future remnant liver, LR: limited resection.
Back to 2017 Posters
|



