|
|
USE OF A CLINICAL PATHWAY IN PATIENTS WITH CROHN'S DISEASE COMPLICATED BY INTESTINAL OBSTRUCTION Zhen Guo*, Weiming Zhu, Jianfeng Gong, Yi Li General Surgery, Jinling Hospital, Nanjing, China
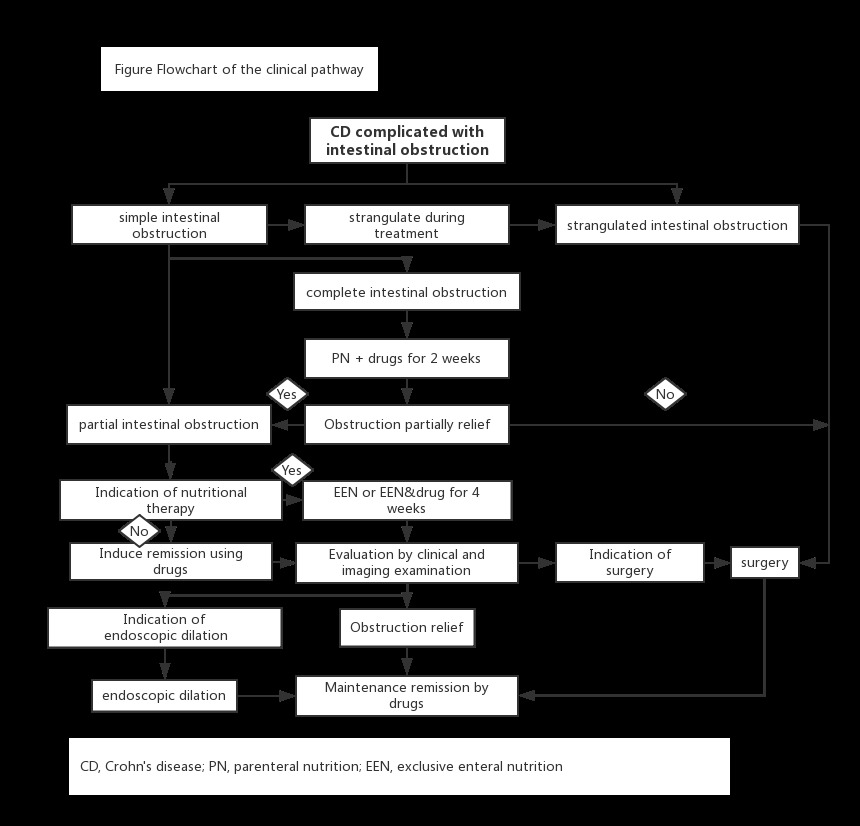
Objectiveÿ¥ Intestinal obstruction is the most common complication of Crohn's disease (CD). The proven of obstruction causes, choosing of therapy strategy, timing of surgery, et al. are complex. A clinical pathway (CP) is the tool to manage the standardization of care processes in order to minimize the hospital stay and improve outcomes. We conducted this study to evaluate the effect of a CP for CD complicated with intestinal obstruction. Methods: Patients with CD complicated by intestinal obstruction from September 2012 to September 2015 were divided into CP group and a non-CP group according to the implementation of a clinical pathway which was developed by our inflammatory bowel disease center based on evidences in February 2014. The clinical outcomes and hospital costs were compared. Results: One-hundred and nineteen patients in CP group and 108 patients in non-CP group were enrolled in the final analysis. The overall completion rate of the clinical pathway was 88.1%. The main reason for dropping out was refusing surgery due to economic issue. Patients' demographics, rate of surgery, and rate of emergency surgery were similar in the two groups, but patients in CP group suffered less 6-month unplanned re-admission (p=0.035). There were 88 patients in CP group and 84 patients in non-CP group underwent intestinal resection respectively. No significant difference was noted between these two groups in terms of rate of stoma, surgical complications, and total hospital stay. However, the CP group had a much lower hospitalization cost (78325 vs 85310, p=0.031) and shorter postoperative hospital stay (10.9d vs 13.2d, p<0.0001). Conclusionÿ¥The clinical pathway for CD complicated with intestinal obstruction used in this study may reduce the 6-month unplanned re-admission, and decrease the postoperative hospital stay and hospitalization expenses in patients requiring surgery.
Back to 2017 Posters |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
© 2026 Society for Surgery of the Alimentary Tract. All Rights Reserved. Read the Privacy Policy.

