
|
 |
Back to 2015 Annual Meeting Program
MiR-650: a Potential Prognostic Biomarker and Therapeutic Target in Non-Metastasis Colorectal Carcinoma
Chunxian Zhou1, 2, Fengyun Cui1, Jiali LI1, Hongguang Zhu1, Ying Wu1, Jiping Wang3, Shuyang Wang*1
1Department of Pathology, Shanghai Medical College, Fudan University, Shanghai, China; 2Department of Pathology, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai, China; 3Division of Surgical Oncology, Brigham and Women's Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA
Background It is estimated that about 26% of stage I and 40% of stage II colorectal cancer (CRC) patients eventually suffered and died from tumor metastasis. There are no validated prognostic biomarkers for the identification of high risk CRC patients to undergo aggressive chemotherapy or target therapy.
Methods Formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded (FFPE) surgical colorectal specimens of 96 stage I/II CRC patients were included in this study. The expressions of 851 human microRNAs were screened with microarray technique and quantitative reverse-transcriptase-polymerase-chain-reaction was used to validate the candidate microRNAs. Kaplan-Meier survival curve analysis was used to evaluate the association between the candidate microRNAs and patients' outcome. Cell Counting Kit-8, transwell insert and tumor xenograft mice model were used to detect the growth and invasion of tumor cells after the addition of microRNA-precursor/-inhibitor of specific candidate microRNAs. Target prediction and luciferase activity assay were applied to predict and validate the target and pathway of the selected miRNA.
Results Five microRNAs (miR-650, miR-146a, miR-365, miR-125a-5p and let-7e) were found to be significantly associated with patients' outcome. Among all the microRNAs, miR-650 was selected for further mechanism exploration. Comparing with control group, the cell growth and invasion in miR-650- precursor group were significantly inhibited (21.0% reduction, and 40.0% respectively, p value=0.045 and 0.008). In the mouse model, the tumor sizes are much smaller in the miR-650 group comparing with control group (87±22 mm3 vs. 57±29 mm3, p=0.05). Furthermore, we found miR-650 could target 3'-UTR of AKT2 directly and inhibit cell migration and invasion via restore E-cadherin junction.
Conclusions Our results indicate that miR-650 impacts on the patient prognosis via inhibiting CRC progression towards AKT2 and E-cadherin. Our study demonstrates the potential of miR-650 as a prognostic prediction biomarker and therapeutic target of non-metastasis colorectal carcinoma.
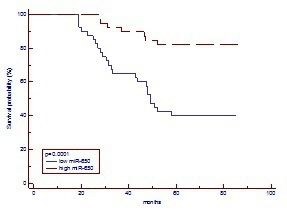
Figure 1. Survival analysis in 88 non-metastasis CRC patients. Patients with lower expression of miR-650 had significantly shorter overall survival 18 months later after resection (HR=4.12; low miR-650, n=40; high miR-650, n=39).
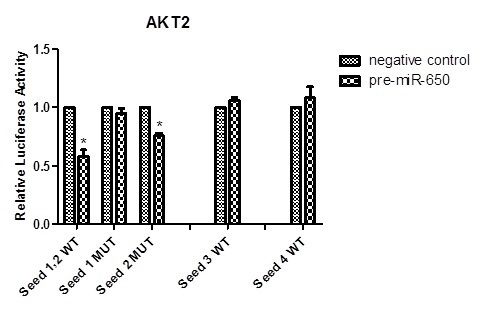
Figure 2. Four 3'-UTR seed sequences of AKT2 were detected by luciferase assays. Comparing with negative control, the luciferase activities of the vector transfected with both miR-650 precursor and seed 1, 2/seed 2 sequences of AKT2 were markedly inhibited (41.9% reduction, and 23.6% respectively, p value =0.02 and 0.002).
Back to 2015 Annual Meeting Program
|



