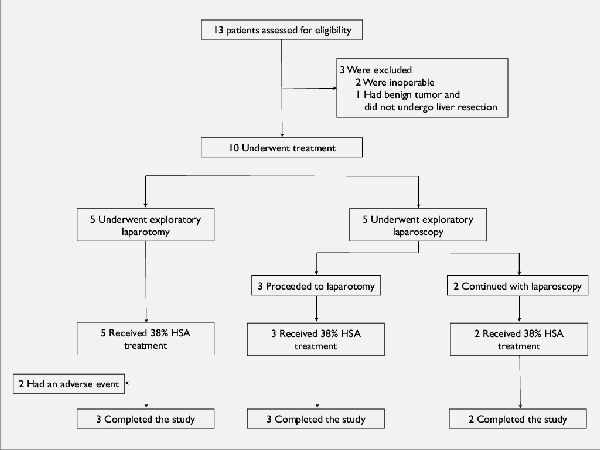
Bleeding from the liver surface is common after hepatic resection and is often controlled using argon beam coagulation (ABC) alone. Animal studies have demonstrated that applying 38% Human Serum Albumin to the resected surface before ABC results in fewer rebleeds. The combination of ABC and albumin (ABCA) has not been reported in humans. The aim of this study was show feasibility of using ABCA for hemostasis of the liver following hepatic resection in humans.Methods:Ten patients underwent liver resection. All ten received ABCA. The liver surface was coated with albumin and coagulated. The liver was covered with gauze for 3 min and inspected for bleeding. This process was repeated if necessary. The number of rebleeding episodes, the time of ABC, overall blood loss, and liver functions were monitored. Patients were followed for at least 6 months. Results:Nine of 10 patients required a single application of ABCA, and one patient required 2 treatments. Average time of ABC use was 5±3 min. Median blood loss was 1100 mL. Liver functions returned to near normal within 4 days of resection.Conclusions:ABCA performed well in controlling hepatic bleeding, much like previous observations in animal studies. Further clinical trials are justified using this technique.
Surgical Metrics
| Patient | Time of ABC(min:sec) | Resected Liver Area(cm2) | Rebleeds | Blood Loss(mL) | Surgical Time(hr:min) |
| 1 | 4:40 | 195 | 0 | 6300 | 14:30 |
| 2 | 3:12 | 36 | 0 | 450 | 3:43 |
| 3 | 13:00 | 145 | 1 | 2100 | 7:40 |
| 4 | 3:40 | 42 | 0 | 450 | 4:36 |
| 5 | 3:54 | 40 | 0 | 1700 | 4:45 |
| 6 | 3:42 | 54 | 0 | 1300 | 9:45 |
| 7 | 5:38 | 96 | 0 | 800 | 4:55 |
| 8 | 7:32 | 108 | 0 | 1300 | 7:10 |
| 9 | 2:15 | 46 | 0 | 100 | 2:30 |
| 10 | 3:45 | 60 | 0 | 900 | 5:13 |
| Median ± StdDev | 3:49 ± 3:10 | 57 ± 53 | 0 ± 0 | 1100 ± 1780 | 5:04 ± 3:30 |
 500 Cummings Center
500 Cummings Center +1 978-927-8330
+1 978-927-8330
 +1 978-524-0461
+1 978-524-0461