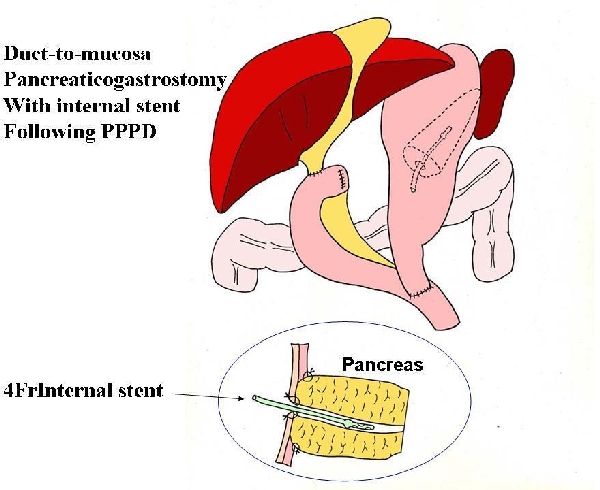
Background and Objectives: Postoperative pancreatic fistula following pancreaticoduodenectomy is relatively common, and remains a major cause of severe complication and surgical mortality. The aim of this study was to evaluate the results of two-layered duct to mucosa pancreaticogastrostomy with internal stent as a method for restoring pancreaticoenteric continuity. Methods: From Dec. 2003 to Oct. 2008, prospectively collected data from 100 consecutive patients who underwent pancreaticoduodenectomy were evaluated. Postoperative pancreatic fistula was assessed using the criteria of International Study Group Pancreatic Fistla (ISGPF). Results: Median drain amylase on day 1 after surgery was 611 IU/L, on day 2 it was 255 IU/L, on day 3 it was 80 IU/L, and on day 5 it was 27 IU/L. Of 100 patients, 13 developed pancreatic fistula; grade A in 11 patients, grade B in 1, and grade C in 1. One re-do operations, but no postoperative percutaneous drainage, and no surgical mortality occurred. By univariate analysis, texture of the remnant pancreas was found to be significantly associated with ISGPF. However, all grade A pancreatic fistula occurred in the patient with soft remnant pancreas and the incidence of clinically significant PF (grade B, C) was 2% (one in soft and one in hard remnant pancreas), there was no significant clinical factor associated with clinically significant pancreatic fistula (ISGPF grade B,C).Conclusions: Two layered duct to mucosa pancreaticogastrostomy with internal stent for restoration of pancreaticoenteric continuity after pancreaticoduodenectomy is associated with a low incidence of clinically significant pancreatic fistula.
 500 Cummings Center
500 Cummings Center +1 978-927-8330
+1 978-927-8330
 +1 978-524-0461
+1 978-524-0461