Background:
A new p53 homologue, p63 regulates differentiation and proliferation in epithelial stem cells. The ΔNp63α isotype functions as a transcriptional regulator and contributes to stem cell status associated with proliferation and tumorigenesis. We hypothesized that p63 plays an important role in the malignant transformation of esophageal mucosa. Methods: Two esophageal cell lines, JA and JB were grown from reflux induced esophageal tumors in rats with capability of in-vitro and in-vivo growth. A mouse monoclonal antibody against all p63 isotypes, a rabbit polyclonal antibody against the C-terminus of p63α (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA) and a rabbit polyclonal antibody against the N-terminus of ΔNp63 isotypes (Oncogene Science Inc. Cambridge, MA) were used to perform immunoblotting. Protein bands were visualized by enhanced chemiluminescence kit (Amersham, Piscataway, NJ). As a p63 negative control we used normal human keratinocyte (NHK) and for p63 positive control an immortalized keratinocyte cell line HaCaT. In addition, protein extract from embryonic retina cell line 911 was used as a negative control for Western Blot. Fluorescence microscopic analysis was performed using confocal microscopy. Results: In the esophageal cancer cell lines immunofluorescent detection with anti-p63 antibodies (4A4) that recognized all known p63 isotypes demonstrated strong p63 staining (red) which associated with the nuclear compartment (blue)(Fig1, A). Moreover by using RT-PCR analysis with pairs of p63 isotype specific primers we identified the major isoform of p63 to be a dominant negative variant of ΔNp63α (Fig1, B). To confirm our results we performed Western blot analysis with detection of p63 protein with isotype specific antibodies for ΔNp63 and p63α. Both antibodies recognized the same band pattern confirming the major variant of p63 expressed in these cell lines is a ΔNp63α (Fig 1C).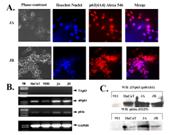
 500 Cummings Center
500 Cummings Center +1 978-927-8330
+1 978-927-8330
 +1 978-524-0461
+1 978-524-0461