# 107584 Abstract ID: 107584 Achalasia and Chest Pain: Effect of Laparoscopic Heller Myotomy
Marco Patti, Silvana Perretta, Piero M Fisichella, Lawrence W Way, San Francisco, CA 94143, CA
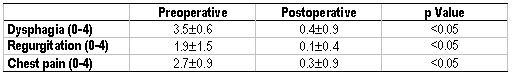
Background. Some patients with achalasia complain of chest pain in addition to dysphagia. Chest pain is thought to be mostly present in young patients who have been symptomatic for a short time, and who often have vigorous achalasia (distal esophageal amplitude ?40 mmHg). While pneumatic dilatation is reported to improve chest pain in 20% of such patients, the effect of laparoscopic Heller myotomy on chest pain is unknown. Aims. The aims were to determine in achalasia: (a) the prevalence of chest pain; (b) the clinical presentation and manometric profile of patients with chest pain; and (c) the effect of laparoscopic Heller myotomy. Patients and Methods. Between 1990 and 2001, 211 patients with achalasia were studied (UGI, EGD and manometry). One hundred and seventeen patients (51%) had chest pain in addition to dysphagia and regurgitation: 63 (54%) of the 117 patients underwent laparoscopic Heller myotomy and Dor fundoplication. Median follow up was 24 months. Results. Age (49?16 vs. 51?14 years), duration of symptoms (71?91 vs. 67?92 months) and presence of vigorous achalasia (50% vs. 47%) was similar in those with and without chest pain. Ten (16%) of the 63 patients with chest pain who underwent Heller myotomy had vigorous achalasia. Postoperatively chest pain resolved in 84% and improved in 11% of patients. There was no difference in outcome between patients with and without vigorous achalasia. Conclusions. These data show that: (a) chest pain is present in half of patients with esophageal achalasia; (b) chest pain is not related to age, duration of symptoms or manometric findings; and (c) laparoscopic Heller myotomy improves chest pain in 95% of patients, regardless of the manometric findings. Thus, laparoscopic Heller myotomy is highly effective in treating achalasia with chest pain.
|
 500 Cummings Center
500 Cummings Center +1 978-927-8330
+1 978-927-8330
 +1 978-524-0461
+1 978-524-0461