# 105432 Abstract ID: 105432 Peptide YY Therapy Ameliorates Acute Pancreatitis by Blocking NF-?B Activation: An In Vitro Model.
Alice K Yu, Linda C Vona-Davis, David W McFadden, Morgantown, WV
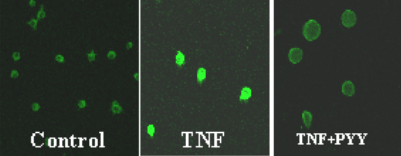
Introduction: Acute pancreatitis (AP) is a common inflammation of the pancreas. It ranges from a mild edematous subtype to severe necrotizing pancreatitis (NP) with systemic manifestations. We have documented that peptide YY (PYY) inhibits pancreatic secretion and ameliorates AP in vivo. Little information exists regarding the effects of PYY on TNF-a induced nuclear factor (NF)-kB activation in NP. We hypothesized that PYY inhibits NF-kB as a mechanism of its improvement of AP. Methods: Rat pancreatic acinar cells (AR4-2J) were cultured using standard techniques. AP was induced by adding TNF-a (200ng/ml). AP was verified by increased amylase release. PYY was added at 50 to 500pM at 30min post TNF-a treatment until cells were harvested for intracellular protein staining of NF-kB p65. Confocal microscopy was used to image cells stained with p65 subunit of NF-kB. Results: TNF-a induced AP 30min after stimulation as demonstrated by amylase production. After 24h, acinar cells stained for NF-kB p65 showed significant staining in the nucleus, while untreated cells showed staining primarily in the cytoplasm. With combined TNF-a and PYY, p65 staining was primarily located in the cytoplasm. Conclusion: We are showing for the first time that TNF-a-induced AP increases nuclear staining with NF-kB p65 subunit in rat pancreatic acinar cells. Treatment with the gut hormone PYY inhibits translocation to the nucleus and offers a therapeutic potential for AP. Further investigations are ongoing.
|
 500 Cummings Center
500 Cummings Center +1 978-927-8330
+1 978-927-8330
 +1 978-524-0461
+1 978-524-0461