# 104504 Abstract ID: 104504 Pancreatic Duct Obstruction Activates Pancreatic Stellate Cells
Shinji Kishi, Yoshifumi Takeyama, Takashi Ueda, Takeo Yasuda, Makoto Shinzeki, Yasuyuki Suzuki, Yoshikazu Kuroda, Kobe, Japan
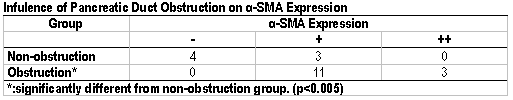
Recently, It has been reported that transformation of pancreatic stellate cells(PSCs) into myofibroblasts is a critical event for pancreatic fibrosis, and the transformation is termed PSC activation. Activated PSCs express a-smooth muscle actin(a-SMA), and a-SMA is available as the marker of activated PSCs. On the other hand, the pancreatic fibrosis induced by pancreatic obstruction is known as chronic obstructive pancreatitis. The aim of this study is to elucidate the relationship of pancreatic duct obstruction and PSC activation. Surgical specimens were obtained from patients with pancreatic carcinoma (n=21, 16 males and 5 females), the non-carcinoma areas were used for evaluation. The mean age of the patients was 64. When the pancreatic duct diameter was over 4mm by preoperative morphological evaluations, including ERCP, CT, MRCP, we defined the case with pancreatic duct obstruction. Accordingly, we divided 21 cases into two groups; 7 cases of non-obstruction group and 14 cases of obstruction group. The expression of a-SMA was evaluated by immunohistochemical study using anti-mouse monoclonal a-SMA antibody (M0851; DAKO, Denmark), and graded into three degrees, which were defined as -, + and ++. In addition, experimental investigation using Male SD rats was performed. The animals were anesthetized and one of the secondary pancreatic duct was ligatured. The expression of a-SMA in the part of the pancreas affected by the duct ligation was evaluated as described above. In clinical investigation, a-SMA expressed in the area existing fibrosis. Expression of a-SMA was more enhanced in obstruction group than in non-obstruction group as shown in the table (p<0.005). In the rat experimental model, a-SMA strongly expressed in the upstream area of obstruction. These findings indicate that pancreatic duct obstruction induces PSC activation.
|
 500 Cummings Center
500 Cummings Center +1 978-927-8330
+1 978-927-8330
 +1 978-524-0461
+1 978-524-0461