# 104332 Abstract ID: 104332 Early MAP Kinase (p38, p44/42 and SAPK/JNK) Activation Is Required for Sublethal Hemorrhage (SLH) Induced Tolerance to Cecal Ligation and Puncture (CLP)
Yvette M Carter, Guoqing Liu, Jun Yang, Adam Fier, William R Gower Jr, Cynthia Mendez, Tampa, FL
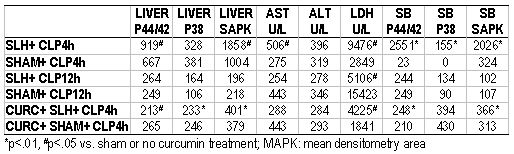
Background: We have developed a model of tolerance in which SLH improves outcome to subsequent sepsis. How SLH affects sepsis related hepatic failure is not known. This study addressed how SLH induced tolerance affected survival, hepatic injury and activation of the inflammatory cascade in a model of polymicrobial sepis, CLP. Methods: Sprague-Dawley rats underwent SLH (hemorrhage to MAP=30mmHg x 15 min, with shed blood returned) or sham operation. After 24hrs, rats had CLP. Survival was determined ( curcumin pretreatment (n=10 each). Liver, small bowel and serum were obtained 4 or 12 hrs after CLP (n=8). Small bowel and liver were analyzed for p44/42, p38 and SAPK/JNK phosphorylation by Western blot, myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity was measured as an index of neutrophil infiltration. Serum was analyzed for hepatic enzymes and TNF. Results: Prior SLH protected rats from CLP associated mortality (21.5 vs. 10.5 hrs, p=.008), and this survival benefit was reversed by curcumin (21.5 vs. 7.5hrs, p=.004). Liver and small bowel MAPK activity were significantly greater in SLH 4hrs post CLP vs. sham. But by 12hrs post CLP, SLH and shams were equivalent. Curcumin significantly decreased hepatic and small bowel MAPK activation 4hrs post CLP vs. SLH alone. TNF levels were higher in SLH rats 4hrs after CLP (108 vs. 38), but there was no difference at 12hrs. Hepatic enzymes (AST & LDH) 4hrs post CLP were significantly greater in SLH rats; however, 12hrs post CLP, LDH was significantly greater in shams. MAPK inhibition with curcumin inhibited the increase in AST & LDH associated with SLH 4hrs after CLP. (TABLE) Conclusion: Early MAPK activation is necessary in SLH induced tolerance to CLP, since the survival benefit is reversed by curcumin. But, this tolerance does not seem to alter MAPK activation in late sepsis. The early rise in hepatic enzymes seen in SLH is likely an index of ischemia and reperfusion. However, SLH's "ischemic preconditioning" seems to protect animals from a later, more severe, sepsis associated liver injury.
|
 500 Cummings Center
500 Cummings Center +1 978-927-8330
+1 978-927-8330
 +1 978-524-0461
+1 978-524-0461