# 100866 Abstract ID: 100866 Activation of Intestinal Arginine Transport by Protein Kinase C Is Mediated by Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases
Ming Pan, Christopher L Wolfgang, Chengmao Lin, Qinghe Meng, Anne M Karinch, Wiley W Souba Jr, Hershey, PA
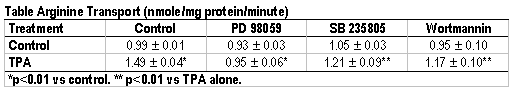
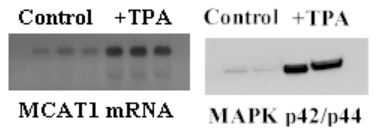
Background: Luminal L-arginine uptake by the intestine can play a pivotal role in regulating nitric oxide (NO) synthesis and immune functions in catabolic states. We have previously showed protein kinase c (PKC) activation stimulates intestinal brush border membrane arginine transport, however, the signaling pathways implicated in this activation have not been studied. The purpose of this study was to investigate the intracellular signal transduction pathways involved. Methods: 3H-L-arginine (50 µM) transport activity, the intestinal arginine transporter MCAT1 mRNA levels and the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) phospho-p42/44 protein levels were measured in cultured intestinal epithelial Caco-2 cells. Cells were treated with phorbol ester (TPA, 0.5 µM), the MAPK MEK inhibitor PD 98059 (50 µM), the p38 MAPK inhibitor SB 235805 (10 µM), and the phosphatidylinositide-3 kinase (PI-3) inhibitor wortmannin (10 µM). Data were analyzed by ANOVA. Results: Specific arginine transporter gene MCAT1 mRNA and MAPK phospho-p42/44 protein levels were stimulated 3- and 2-fold in phorbol ester treated cells respectfully, compared to control group (see figure). Intestinal arginine transport activity was stimulated by continuous phorbol ester exposure (>12 hours). This phorbol ester induced arginine transport activity was blocked individually by PD 98059, SB 235805, and wortmannin (see table). Arginine transport activity in cells treated with individual inhibitor alone did not differ from control cells treated with vehicle. Conclusions: Activation of arginine transport in Caco-2 cells by phorbol ester occurs via signaling pathways that lead to transcription of the arginine transporter gene. PKC, MAPK MEK, p38 MAPK, p42/44 MAPK and PI-3 are key intracellular regulators involved in this signal transduction cascade.
|
 500 Cummings Center
500 Cummings Center +1 978-927-8330
+1 978-927-8330
 +1 978-524-0461
+1 978-524-0461