# 100799 Abstract ID: 100799 Modulators of Ceramide Metabolism Sensitize Colorectal Cancer Cells to Chemotherapy: A Novel Treatment Strategy
David A Litvak, Anton J Bilchik, Myles C Cabot, Santa Monica, CA
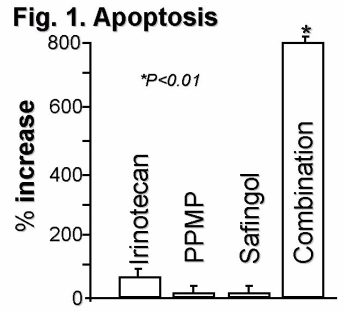
Introduction. Resistance to chemotherapy is a major treatment obstacle for advanced colorectal cancer (CRC). We have shown previously that chemosensitivity correlates with formation of the apoptosis-inducing lipid ceramide, while chemoresistance correlates with formation of the non-cytotoxic metabolite glucosylceramide (GlcCer) in several types of cancer cells. Our study assessed the role of ceramide in chemotherapy-mediated CRC cell death. Methods. Using the human CRC cell lines HT-29 and CeNU (established in our lab), we assessed the effects of irinotecan (CPT-11) on ceramide metabolism, cell viability, and apoptosis. Fumonisin B1 (FB1) was used to block ceramide synthesis, and 1-phenyl-2-palmitoylamino-3-morpholino-1-propanol (PPMP) to block metabolism of ceramide to GlcCer. Safingol was used to block secondary ceramide-activated protein kinase-C-mediated proliferative pathways. Statistical significance was assessed by ANOVA. Results. Irinotecan caused a 300% increase in ceramide (p<0.05), which preceded apoptosis in both cell lines; however, cell viability was restored by adding FB1 to block ceramide synthesis. The ~40% of cells that remained viable after treatment with irinotecan demonstrated increased levels of GlcCer (~50% over untreated cells; p<0.05). When GlcCer synthesis was blocked with PPMP in HT-29 cells, levels of ceramide were significantly increased and cell death was enhanced. Moreover, when PPMP and safingol were combined with irinotecan in both cell lines, cell death was increased in a synergistic fashion, compared to irinotecan alone (p<0.01) (Fig. 1; HT-29 cells). Conclusions. The cytotoxic effects of irinotecan are mediated by ceramide and may be enhanced by blocking ceramide metabolism. Targeting ceramide metabolism is a novel and potentially effective treatment strategy for advanced CRC.
|
 500 Cummings Center
500 Cummings Center +1 978-927-8330
+1 978-927-8330
 +1 978-524-0461
+1 978-524-0461